Dilated uterine tube. Symptoms and signs of inflammation in the fallopian tubes: how to treat and what drugs to take
The medical name for the inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes is salpingitis. This common gynecological disease is one of the factors of female infertility. The main cause of inflammation is the activity of pathogenic bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci or mycoplasmas. Another cause is chlamydia, gonorrhea and other STDs.
The disease is serious and quite dangerous: purulent discharge, which often occurs during inflammation, can spread to healthy neighboring organs of a woman. In addition, with salpingitis, a rupture of the fallopian tube is also possible, which causes peritonitis.
Although this life-threatening condition occurs quite rarely.
How does inflammation of the fallopian tubes manifest itself, the symptoms and treatment of this pathology, how is it carried out? What folk remedies can help? Let's talk about it:
Varieties and symptoms of salpingitis
Doctors distinguish two types of pathology: acute, subacute and chronic.
The acute form is diagnosed especially often. It is characterized by swelling of the fallopian tubes, the release of a thick fluid that sticks together their walls. Also, their cavities can be filled with purulent contents, which provokes their clogging.
An acute process is accompanied by fever, chills, and poor health. There are pulling, dull pains in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sacrum and rectum. characteristic feature diseases are serous-pustular discharge from the vagina and urethra, there are sharp pain during sex.
There may be problems in the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation, diarrhea. Frequent urge to urinate with little urine output. The process itself is accompanied by soreness (cutting).
In addition, signs of general intoxication are observed, emotional and neurotic disorders occur.
The subacute form is characterized by an improvement in well-being, a decrease in painful symptoms. This form is evidenced by the presence of subfebrile body temperature (constantly elevated temperature - 37.1 ° C-37.5 ° C).
Chronic inflammation continues for a long time. It is characterized by the symptoms listed above, but much less pronounced than with acute inflammation. There is a very satisfactory general state, the temperature does not rise. However, persistent pain persists.
At the end of the remission period and with the onset of exacerbation of chronic salpingitis, its symptoms intensify. An exacerbation can be caused by hypothermia, physical overwork, stress, or an attached infection.
For example, if pyosalpinx develops against the background of salpingitis, fever, chills develop, signs of irritation of the peritoneum appear. In case of rupture of the pyosalpinx, purulent diffuse peritonitis develops.
Other types of salpingitis
- Gonorrheal. It is characterized by lesions (in addition to the fallopian tubes) of the urethra, cervical canal, as well as paraurethral passages, Bartholin glands and rectum.
- Chlamydial. It is characterized by the development of a destructive lesion of the fallopian tubes. There are not very pronounced symptoms of urethritis, cervicitis and endometritis. The transferred chlamydial form of salpingitis often causes the development of ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
- tuberculous. It usually has a mild chronic form. The period of exacerbation is usually observed in the clinical caseous form (pneumonia with a predominance of cheesy necrosis).
Note that salpingitis itself is rarely diagnosed. Usually it is joined by adnexitis (inflammatory process in the ovaries) or endometritis (endocervicitis) - an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa.
How is inflammation of the fallopian tubes corrected, what treatment of salpingitis is effective?
When prescribing therapeutic treatment, the nature of the disease, the stage of the inflammatory process, the individual characteristics of the patient's body (age, general health, contraindications to taking the drugs used, etc.) are taken into account. To prescribe adequate, effective treatment, it is very important to conduct timely, accurate diagnosis.
In the presence of an acute form, inpatient treatment is indicated. After the examination, clarification of the etiology of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed: Penicillin, Tetracycline, Cephalosporin. If necessary, other antibacterial drugs are also prescribed: Fluoroquinolones, Aminoglycosides and Macrolides.
In addition, according to indications, antifungal agents, drugs - Nitrofurans, NSAIDs are prescribed. The complex of treatment includes infusion therapy, autohemotherapy. The therapy is complemented by the introduction of Cocarboxylase, Lidase and vitamins. Exacerbation of chronic salpingitis is treated in a similar way.
In the chronic form, physiotherapy methods are used: electrophoresis, UHF, magnetotherapy and ultrasound. Apply diadynamic therapy and hydrotherapy, in particular, radon and sulfide baths.
To relieve painful symptoms, eliminate the risk of possible pathological changes, acupuncture is prescribed (indications and contraindications must be taken into account). The period of rehabilitation treatment is supplemented with heat treatment.
With chlamydial form of salpingitis, treatment is carried out with the help of Metronidazole. Tuberculosis and gonorrhea are treated according to the general scheme of therapy for these diseases.
If an extensive accumulation of pus inside the fallopian tube is diagnosed, an abscess is opened, drained and cleansed using a lower median laparotomy.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes - alternative treatment
In addition to the main treatment, you can use effective, proven folk recipes previously agreed with the attending physician. Here are some recipes:
In this disease, healers recommend using an alcohol tincture of Echinacea purpurea: pour crushed flowers into a jar (25 g dry or 50 g fresh). Add half a liter of vodka. Close the jar tightly, put it in a dark room for 2 weeks. Strain the finished medicine, squeeze. Keep cold. Take 6 drops per 1 tablespoon of water, every 4 hours. Treatment - 4-5 days. Please note: Dr. Theiss echinacea tincture is on sale.
It is useful to take healing baths with an infusion of a mixture that includes juniper stalks and fruits: pour 50 g of raw materials into a bucket or large pot, add 5 liters of boiling water. Close the lid, wrap. After 2 hours, pour through a colander into a bathtub filled with water. Take a warm bath for 20 minutes, 3-4 times a week.
You can supplement the treatment of salpingitis with therapeutic tampons: soak ordinary hygienic tampons with fresh plantain juice or perennial aloe. Insert into the vagina overnight.
You need to understand that folk recipes will bring quite a tangible therapeutic effect only if they are used in combination with traditional treatment prescribed by the attending physician.
To avoid possible serious complications of the disease, treatment should be started as early as possible. Therefore, at the first signs of the inflammatory process, hurry up with a visit to the doctor. Be healthy!
It is considered a fairly common disease of the female reproductive system, which can lead to tubal infertility.
General information
Inflammation of the fallopian tube is a pathology of a gynecological nature, in the absence of treatment of which the process flows into a chronic form. Currently, experts distinguish the following types of it:
- Salpingitis. This is inflammation, the formation of which occurs due to the penetration of infectious agents into the fallopian tubes. Neglect of the disease or its incorrect treatment can lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes, female infertility.
- Salpingoophoritis. This is an inflammatory process that is formed on the uterine appendages due to the active life of pathological microorganisms (staphylococcus aureus, tuberculosis bacteria).
Most often, infection occurs in an ascending way, that is, through the vagina. Then the pathogenic flora moves along the cervical canal, the end point of this “journey” is the fallopian tubes. Inflammation of the fallopian tube begins with its mucous membrane. Then the pathological process spreads to deeper layers.
Immediate seeking help from a doctor and competent therapy guarantee a complete recovery. The most favorable prognosis is considered when the inflammation did not provoke obstruction of the tubes. IN this case treatment allows you to fully restore reproductive function.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes: causes
- Various infections (gonococci, chlamydia, Trichomonas).
- Promiscuous sexual relations.
- Non-traditional form of sexual intercourse.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Outside intervention in the female environment ( C-section, cervical injury, abortion).
- Frequent stress.
Clinical picture
As practice shows, signs of inflammation of the fallopian tubes can vary depending on the specific type of pathology.
The acute form of salpingoophoritis is characterized by the appearance of pain discomfort in the lower abdomen and lower back. In addition, many women note fever, general deterioration, chills, excessive sweating. In rare cases, purulent discharge from the vagina is possible.
The chronic form of salpingo-oophoritis is characterized by the occurrence of dull aching pain in the lower abdomen and in the vagina. Women complain of problems with the menstrual cycle, decreased libido and discomfort during direct sexual intercourse. Analyzes show a decrease in the level of female hormones and the formation of ovarian hypofunction.
On initial stage The development of salpingitis is characterized by pain discomfort in the lower abdomen and problems with urination. As the disease progresses, these symptoms are added from the vagina, and sexual intercourse is accompanied by severe pain. In some cases, there may be a slight increase in temperature, general malaise and periodic bouts of weakness. 
Diagnostic measures
If you suspect an inflammation of the fallopian tubes, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. At the appointment, the specialist conducts a gynecological examination, collects a complete history. To determine the specific form of pathology, a number of additional tests may be required, including microbiological examination of the uterus, vagina, and urethra. Ultrasound allows you to get the most informative picture of the condition and differentiate inflammation of the fallopian tubes. The symptoms described in this article do not always indicate precisely this pathology.
Determination of the final diagnosis is impossible without laparoscopy. This method allows you to visualize the internal organs and assess their condition. Laparoscopy is a mini-surgery that is performed using local anesthesia. The laparoscope is a tube with multiple lenses that is inserted directly into the abdominal cavity through small incisions. With it, the doctor can examine the fallopian tubes, determine their condition, the presence of an inflammatory process and pus. 
Conservative therapy
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes should not be left without due attention. Treatment of this pathology is possible only in stationary conditions. Therapeutic tactics largely depends on the results of diagnosis, the cause and form of the inflammatory process, as well as the presence of concomitant complications. Of course, advanced cases require a more serious approach to treatment.
With salpingoophoritis, a complex drug therapy, which includes taking antibiotics ("Azithromycin", "Cefotaxime", "Gentamicin") and immunomodulators. Depending on the condition of the patient, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs may be additionally prescribed.
Antibiotics are also prescribed for salpingitis. To prevent possible dysbacteriosis, antibacterial therapy is combined with the use of antifungal agents (Fluconazole, Ketoconazole) and probiotics (Linex). 
When is surgery necessary?
If conservative treatment is ineffective, doctors recommend surgery for all patients diagnosed with inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms of pathology in the absence of therapy can significantly reduce the quality of life.
In some cases, even surgery is contraindicated. If the patient is obese, she is diagnosed with acute diseases infectious nature, it is better to refuse surgical intervention.
The operation involves the removal of a part of the fallopian tube, cleaning it from existing pus and disinfection. If there is no possibility to eliminate the purulent focus, the doctor most often decides to remove the entire uterine appendage.
Removal of the fallopian tubes during inflammation is carried out through laparoscopic surgery. The surgeon initially makes several punctures in the abdominal wall, through which instruments for manipulation are subsequently inserted. The procedure itself is considered low-traumatic, recovery takes place without serious complications. After surgery, some patients complain of nausea and bloating. As a rule, such symptoms disappear after 2-3 days and do not require special treatment. 
Treatment with folk remedies
Strengthen the therapeutic effect in the diagnosis of "inflammation of the fallopian tubes" can be folk remedies. You should first consult with a gynecologist on this issue. Below we list the most popular recipes for alternative medicine:

What is the danger of pathology when carrying a child?
And the fallopian tubes are quite rare during pregnancy. If this happens, the consequences can be very serious. For example, if salpingitis is diagnosed in a pregnant woman in the early stages, the pathology can lead to a miscarriage. In the second and third trimesters, it often ends with the death of the fetus.
After the doctor confirms such a diagnosis, the future woman in labor is immediately hospitalized and appropriate therapy is prescribed.
In women who have already suffered inflammation of the fallopian tube, the likelihood of infertility or ectopic pregnancy increases several times. In order to avoid such complications, patients are advised to undergo a special examination. According to its results, one can judge the patency of the pipes and the possibility of naturally conceiving a baby. In especially serious cases, the only option is in vitro fertilization. 
Prevention
Prevention of any disease, and inflammation of the fallopian tube is no exception, allows you to prevent the development of the disease and increase the likelihood of a speedy recovery if the infection still managed to enter the body. Among the main measures aimed at preventing this pathology, experts call the following:
- Usage modern means contraception during intercourse.
- Elimination of stress and constant overwork.
- Prevention of hypothermia of the body.
- Healthy lifestyle and balanced diet.
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
- Timely treatment of all diseases.
Conclusion
Any inflammatory process in the body requires timely treatment, especially for the organs of the female reproductive system. Neglect of health can negatively affect the ability to naturally conceive a child. That is why it is so important to seek qualified help and undergo a course of treatment when the first signs of this pathology appear. Be healthy!
Such a disease is called salpingitis in medicine, various infections (chlamydia, gonococci, escherichia, etc.) lead to its appearance. Abortion, childbirth, menstruation can provoke inflammation of the tubes. In some cases tube inflammation treatment may be required in parallel with the treatment of ovarian disease, which is called oophoritis.
Symptoms of the development of inflammation of the tubes
The main signs that indicate the possibility of the initial stage of the disease are:
Pain when urinating;
The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen;
Profuse purulent discharge;
Pain during intercourse.
If a sexual partner currently or in the past had a gonococcal infection (gonorrhea), then this may serve as a signal for a mandatory examination, since inflammation of the tubes in women can be asymptomatic for quite a long time, and lead to serious consequences.
Forms of inflammatory diseases of the fallopian tubes and their manifestations
The disease usually occurs in:
- subacute,
- acute
- and chronic form.
At the acute stage there is an increase in temperature, there is pain in the lumbar region and abdomen.
When chronic stage with inflammation in the tubes, pain is observed with the formation of a sactosalpinx - saccular inflammatory formations.
In some cases, inflammation of the tubes can occur along with the inflammatory process in the ovaries (oophoritis).
Symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the tubes and ovaries in parturient women
The occurrence of such complications in the postpartum period is quite rare. However, when this pathology occurs, the appendages on one side are more often inflamed.
The clinical symptoms of oophoritis are similar to those of endometritis.
- The continuation of oophoritis is salpingoophoritis (inflammation of the ovary along with the fallopian tube), respectively, the clinical picture increases the symptoms.
- There is a deterioration in the condition, manifested by pain in the lower abdomen and in the iliac regions.
- The temperature rises, with purulent-septic inflammation, the temperature takes on a hectic character and stays at high numbers for a long time.
Inflammation of the tubes: treatment of the disease
The treatment of inflammation largely depends on the stage of inflammation, the nature, as well as the individual tolerance of drugs. An important role in the treatment is its correct and timely diagnosis.
The lack of necessary treatment for salpingitis can lead to adhesions in the pipes, which can cause them to become obstructed and lead to complications that make it difficult to treat inflammation. Never self-medicate! This occupation can lead to the transition of inflammation of the pipes into a chronic form. There will be complications and irreversible processes with salpingitis, after which surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
And in this case, the prognosis for the complete restoration of reproductive function and working capacity is not always favorable.
Treatment of inflammation of the tubes and ovaries in parturient women
With timely and adequate treatment of inflammatory diseases of the tubes and ovaries, the inflammation process is stopped quickly enough. Treatment of inflammation of the tubes and ovaries - broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, detoxification therapy, drugs that stimulate the body's defenses and immune forces are used. With a significant purulent accumulation in the fallopian tube or ovary, drainage of the abscess is necessary. An abscess is opened using a lower median laparotomy: it consists of opening a purulent formation (conglomerate) with subsequent removal of the appendages and leaving the drainage in the abdominal cavity. According to the left drainage, you can monitor the amount of inflammatory discharge and inject various kinds of drugs into the affected area:
- antibiotics,
- antiseptics,
- proteolytic enzymes).
Causes and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the fallopian tubes
Salpingitis is characterized by various infections (escherichia, chlamydia, gonococcus, etc.), the provoking factor of which can be
- childbirth,
- abortion,
- menstruation.
Inflammation of the tubes can be caused chronic diseases appendages. With inflammation in the tubes, the disease primarily affects the mucous membranes of the uterine appendages, after which the inflammatory process of the muscular membrane of the uterine tubes develops.
Disease prevention includes:
fight against abortion
prevention of post-abortion and postpartum complications,
keeping a strict record of contraindications for various intrauterine interventions,
timely elimination of foci of infections
and effective treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease. Also of no small importance in the prevention of the disease is the teaching of girls and women to hygiene.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes is called salpingitis, and is one of the most common causes of infertility in women.
In very rare cases, the fallopian tubes rupture and cause a dangerous infection in the abdomen called peritonitis.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes, also known as inflammation of the fallopian tubes, is the result of an abnormal growth of harmful bacteria in the fallopian tubes. The female reproductive system includes a pair of fallopian tubes. These tubes, also known as fallopian tubes or oviducts, are very thin tubes lined with ciliated epithelium. They connect the ovaries to the uterus, and eggs travel through them. The fallopian tubes play an important role in fertilization. Just like other systems present in the body, they can become inflamed for a number of reasons.
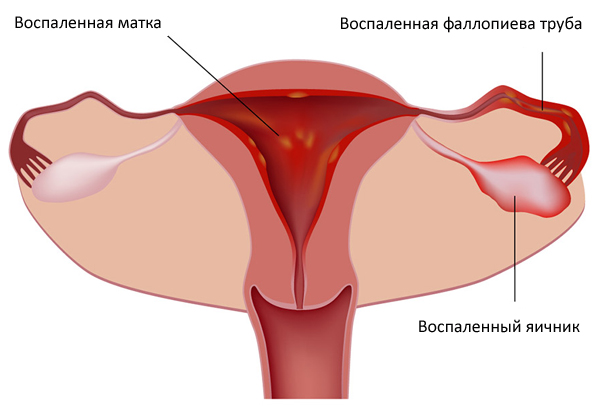
Another name for salpingitis - pelvic inflammatory process. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, two types of this disease are distinguished - acute and chronic salpingitis. In acute salpingitis (or acute inflammation of the fallopian tubes), the fallopian tubes swell and secrete fluid, which causes their walls to stick together. They can also swell and fill with pus. All this can lead to blockage.
If the inflammation is chronic, it can persist for a sufficiently long period of time, accompanied by the appearance of milder and less noticeable symptoms than with acute inflammation. The symptoms of salpingitis require urgent medical attention, and if left untreated, permanent damage to the fallopian tubes can result.
Causes of salpingitis
First, inflammation usually forms in the vagina, from where it gradually moves up towards the fallopian tubes. Since the infection spreads through the lymphatic vessels, if one fallopian tube becomes inflamed, the other may also become inflamed. The most common cause of inflammation is the growth and spread of harmful bacteria such as streptococci, mycoplasmas, and staphylococci.
Another reason is infection with sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea etc. Complications of inflammation of the fallopian tubes include ectopic pregnancy and the possibility of infection spreading to nearby organs such as the ovaries, uterus, etc. Inflammation of the fallopian tubes can also lead to the formation of scars in them, which can completely block them. In addition, as a result of the formation of pus in the ovaries, complications such as the formation of underdeveloped eggs sometimes occur, which leads to infertility.
Symptoms of inflammation of the fallopian tubes

If the inflammation is mild, there are almost no symptoms. They become noticeable after menstruation. Some of the symptoms are similar to those of gonorrhea (a sexually transmitted disease).
- Abnormal color and smell (usually yeasty) of vaginal discharge
- Discomfort and pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Malaise, nausea and vomiting
- Fever and severe headache
- Spotting between periods
- General weakness
- Pain during menstruation
- Severe pain in the abdomen on both sides, especially in the lower part
- Pain during ovulation
- Lower back pain
Treatment of inflammation of the fallopian tubes
Treatment of inflammation of the fallopian tubes depends on the severity and the cause of its symptoms. To determine the severity of the inflammation, it may be recommended to take a cervical smear, a smear from the vaginal mucosa, as well as blood for analysis. Doctors often prescribe antibiotics to treat inflammation and kill bacteria. In severe cases, it may be necessary to undergo surgery to clear the blockages of the fallopian tubes and remove their inflamed parts in order to suppress the spread of infection.
In order to prevent inflammation of the fallopian tubes and other organs of the reproductive system, it is necessary to take preventive measures against infection with sexually transmitted diseases. If any anomalies or even the mildest symptoms appear that may be associated with inflammation of the fallopian tubes, you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. Be healthy!
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes (video)
- Endosalpingitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes. Concomitant symptoms: hyperemia, swelling, deterioration of microcirculation with further cell deformation. The process most often develops on both sides, although a unilateral lesion is also possible, in particular when using an intrauterine device. Inflammatory process affects the muscular and serous membrane of the tubes, then the infection spreads into the abdominal cavity and causes damage to the epithelium of the ovary and the adjacent peritoneum.
- Salpingo-oophoritis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the uterine appendages, fallopian tubes and ovaries. The consequence of such a disease may be the inability to fertilize. Such a disease may be the result of pathologies of the pelvic organs, in particular, if the disease has not been completely cured. This pathology is characterized by the formation of infiltrates, dysfunction of the mucous membranes and muscular membranes of the fallopian tubes, narrowing of the lumen of the vessels. Symptoms: dull or aching pain in the fallopian tubes and in the lower abdomen, groin and vagina.
- Oophoritis is inflammation of the ovaries. Often occurs along with inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Causes: abortion, menstruation, childbirth in combination with infections of various origins. The main signs of the disease are urination disorders, pain in the fallopian tubes, lower abdomen, purulent discharge, discomfort or pain during intercourse. Treatment is prescribed depending on the nature and course of the disease. The patient is prescribed rest, in the first days ice can be applied to the lower abdomen, the use of painkillers and antibacterial drugs, sulfonamides, calcium chloride is indicated, physiotherapy is prescribed (for example, local application of quartz).
- Fluid in the fallopian tubes (simple or follicular). In the tubes, from one to several closed cavities are formed, in which the secret of the fallopian tubes accumulates, as a result of which the walls of the tubes stretch and become thinner. In the presence of adhesions, the fluid accumulates again, causing inflammation in all the genital organs. The fluid that appears in the pipes causes bacteria to multiply and is a constant causative agent of infection. With prolonged hydrosalpinx, the formation of connective tissue strands occurs, provoking chronic pain.