Gallbladder stones symptoms treatment. Causes, symptoms and treatments for gallstones
An article about the symptoms of gallstone disease, diet therapy for it and ways to prevent the formation of stones in the gallbladder.
Gallstones affect one in four adult men and one in three adult women in Europe and America. For many, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time, and they do not even suspect that they need any treatment.
But if the bladder becomes inflamed, or the stones begin to move, the patient experiences pain and discomfort. Difficult questions arise before him: how to cure gallstone disease, is it possible to do this without surgery.
What are the symptoms of a gallstone?
Gallbladder stones are diagnosed in children and adults, men and women, generally healthy or with a "bouquet" chronic diseases. However, a certain trend is still emerging:
- In most cases, gallstone disease is found in people after 40 years of age.
At this age, more women than men suffer from the disease. - Usually, gallstones are found in overweight people.
In addition to being overweight, risk factors for the formation of stones are:
- Irrational nutrition. Excesses in both directions are harmful - both overeating and undernutrition.
- Elevated cholesterol.
- Endocrine diseases and hormonal disruptions, including during pregnancy.
- Diseases of the pancreas.
- Physical inactivity.
- Other.
IMPORTANT: Stones are compacted particles of bile that have a different composition. Usually, they include the bile pigment bilirubin, cholesterol and calcifications.
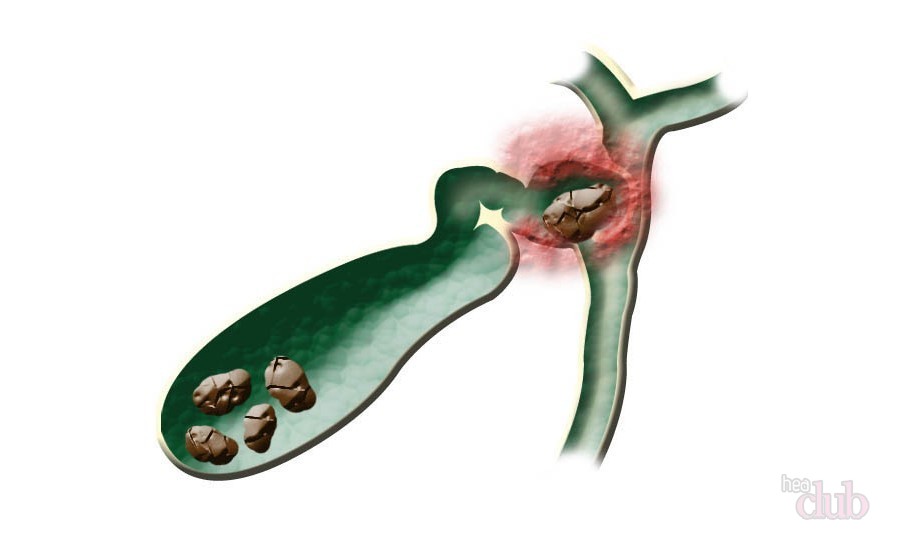
Small calculi can "swim" in a gallbladder filled with bile for quite a long time, without making themselves felt. But only until, due to strong physical activity, during a trip in transport, after a magnificent feast, they do not set in motion. Then:
- Their sharp ends scratch and irritate the inner surface of the gallbladder, causing its acute inflammation. This is a separate disease, acute cholecystitis).
- They can move into the ducts that connect the organ to the liver, causing bile stasis and an acute attack of colic.
- Inflammation from the gallbladder spreads to organs - neighbors: the pancreas, stomach and intestines.
In many patients, the disease manifests itself unexpectedly, with sharp pain during an attack of biliary colic:
- It hurts in the upper abdomen, usually in the right hypochondrium.
- The pain, as it were, spreads through the body - radiates to the right: to the back, collarbone and arm.
- There is a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Nausea and vomiting begin.
- Pain when touching the area of the gallbladder.
- Yellowing of the eyes and skin.
In the best case, the attack ends by itself when the stone, capable of passing through the ducts due to its size, enters the duodenum and is evacuated from the body with feces. Too large calculi can block the bile ducts.
IMPORTANT: There are also certain signs by which gallstone disease can be suspected even before its symptoms appear. When they appear, it is advisable to undergo examinations, and in case of confirmation of suspicions, and appropriate treatment.
These signs are:
- heaviness under right rib
- bitterness in the mouth
- heartburn
- belching
- periodic nausea
Types of gallstones and their diagnosis
As mentioned above, stones in the gallbladder can have a different composition.
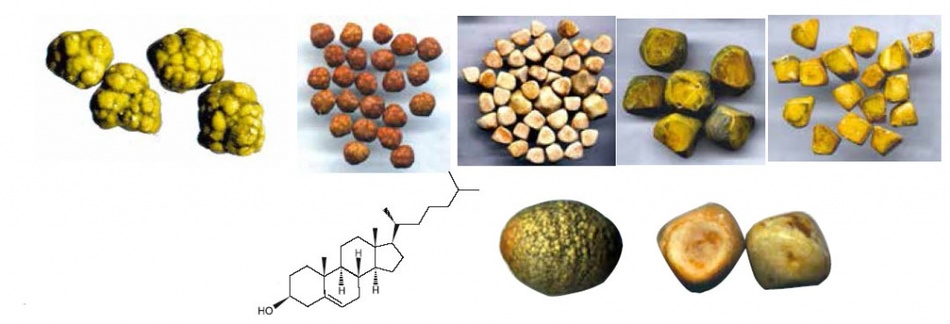
Firstly, they can be single-component, but these are extremely rare. These are the stones:
- Cholesterol. They are usually round and small (up to 1 cm). The reason for their appearance is proper nutrition and metabolic disorders.
- Pigmentary (bilirubin). There are a lot of such pebbles of a very small size in the gallbladder and its ducts.
- Lime (calcifications). Formed from calcium salts.
Secondly, calculi can be with mixed compositions, and these are found in 80% of patients. Their composition is as follows:
- cholesterol - 90%
- bilirubin - up to 5%
- calcium salts - up to 3%
- other substances
Mixed stones come in various sizes, and the larger they are, the more dangerous the disease.
IMPORTANT: Medicine knows cases when the entire cavity of the gallbladder was occupied by one large calculus weighing up to 100 g.
The shape of the stones formed in the gallbladder can be:
- round
- barrel-shaped
- ovoid
- multifaceted
- other
After examining a doctor - a gastroenterologist who observes pain in the abdomen in the gallbladder area, a patient with suspicion of stones is sent for examination:
- Blood tests. The general will show elevated leukocytes and ESR, biochemical - elevated cholesterol and bilirubin.
- Holitsestography (x-ray examination of the bile with contrast).
- ultrasound. This method is very effective, it can be used to determine not only the presence of stones, but their number, shape, size and composition.
- MRI and CT. Modern and very informative methods.
How do gallstones come out of the gallbladder?
If the stone has a significant size, its exit from the gallbladder is accompanied by an attack of colic.
- The calculus, driven by bile, enters the mouth of the duct. There is a blockage and a violation of the outflow of bile.
- Under the action of calculus and bile pressure, the mouth of the duct is stretched, which causes a sharp pain to a person.
- The stone is pushed through the ducts and enters the duodenum. The pain releases the person, he feels relief.
- The calculus comes out along with the feces.
Gallbladder stones during pregnancy
In pregnant women, gallstone disease is found quite often. Because:
- During this period, the woman undergoes a thorough medical examination. She had stones before, but they did not make themselves felt. Unfortunately, few young women are examined for preventive purposes, so no one suspected the disease before pregnancy.
- Pregnancy provoked the formation of stones. The fact is that during the bearing of a baby in the body of a woman, the hormone progesterone is produced in increased quantities, one of the functions of which is the relaxation of smooth muscles. The outflow of bile under its influence becomes slower, due to its stagnation and stones are formed.
For a woman who was diagnosed with gallstone disease during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes:
- diet therapy
- antispasmodic type
- easily choleretic if the stones are small
IMPORTANT: If the duct is blocked by a calculus during pregnancy, laparoscopic removal of stones from the gallbladder is possible.
Is it possible not to have surgery for gallstones?
If stones are found in the gallbladder, the doctor will immediately tell you about the operation to remove them and the bladder itself. Of course, this prospect is scary. You can try to cope without it.
IMPORTANT: You can postpone the operation only if the disease is asymptomatic, there are few gallstones, their size is small.
If surgery cannot be avoided, most often cholecystectomy is performed by laparoscopy, which is considered the least traumatic. But sometimes classical open operations are also performed.
VIDEO: Laparoscopy: surgery to remove the gallbladder
Nutrition menu for gallstones: what is possible and what is not

Patients with cholelithiasis are shown therapeutic diet No. 5. Its basic principles are as follows:
- Fast food and snacks prohibited.
- Bakery, confectionery should be limited to a minimum.
- soda, low-alcohol and alcoholic drinks, coffee are prohibited.
- Recommended there are warm first courses. If they are in meat broth, the meat should be lean and the broth second.
- Vegetables are also the basis of the diet. You can eat everything except raw cabbage and legumes.
- Necessary consumption of fresh fruits and berries. These are apples, bananas, melon, strawberries, etc.
- Sharply limited intake of fried and fatty foods, in particular, of animal origin, which is a provocateur of high cholesterol and, as a result, the formation of gallstones.
- Recommended fractional and frequent consumption of food, 4 to 6 times a day. This ensures optimal movement of bile.
- Concerning consumption food: fats need to be reduced. The rate of carbohydrates (complex) on diet number 5 is up to 350 g, fats and proteins - up to 90 g.
- Reduce your daily intake calorie intake is not necessary. With gallstones, a person should consume about 2500 kcal per day. If he has excess weight, this moment is negotiated with the doctor.
- Doctors also advise introduce fiber and healthy fats in the form of bran, Omega3 nutritional supplements into the diet.
VIDEO: Diet for gallstone disease
Prevention of gallstones

The health of all digestive organs, however, of the whole organism, is interconnected. Therefore, the prevention of the formation of stones in the gallbladder is a general recovery and strengthening, which includes:
- healthy eating
- gradual weight loss if needed
- sufficient physical activity
- timely detection of health problems and their correction
Cholelithiasis- a general somatic disease caused by the formation of stone-like formations (calculi) in the gallbladder, ducts as a result of a violation of the biomechanisms of certain metabolic reactions. The incidence of the disease ranges from 10% for the adult population to 30% for the elderly and senile.
The disease develops for a long time - for several years, during which a polymorphic symptomatic picture is observed. To remove stones, conservative methods are used (drug dissolution, crushing by shock wave or laser exposure). In advanced cases, the removal of stones is carried out through surgical intervention.
Causes of stone formation in the gallbladder
The main factors causing the onset and further development of pathology are the production of bile supersaturated with cholesterol, a shift in the equilibrium balance between the activity of antinucleating and pronucleating biocomponents against the background of a deterioration in the contractility of the gallbladder.
This problem may be the result of various autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, hemolytic anemia, granulomatous colitis, various forms of allergies, liver cirrhosis, and others). However, the most probable causes formation of calculi are considered as follows:
- The presence of inflammation in the bile ducts, bladder.
- genetic predisposition.
- Hemicolectomy (total or subtotal).
- Obesity.
- Postponed surgical operations on the organs of the digestive tract.
- Dyskinesia (functional disorders of motility) of the biliary tract.
- periods of pregnancy.
- An unbalanced nutritious diet, which is based on cholesterol-containing foods, poor in plant fibers.
- Lesions of the hepatic parenchyma, characterized by infectious-toxic etiology.
- cholesterosis.
- Sudden weight loss, starvation.
- The presence of a syndrome of impaired absorption.
- Taking certain medications (including oral contraceptives).
- Cholecystitis (xanthogranulomatous, chronic form).
- Flatulence.
- Age changes.
- Violations of the functions of the endocrine system.
- Sedentary lifestyle, hypodynamia.
Stone formation in the cavity of the bladder and bile ducts can be provoked by mechanical causes: the presence of tumor-like neoplasms, adhesions, edema, narrowing and kinks of the ducts. In addition, the presence of congenital anomalies is not excluded - cysts of the main bile duct, duodenal diverticulum.
Symptoms of gallstones
For cholelithiasis, initially (the first 4-8 years), an asymptomatic course is characteristic. The time of onset of symptoms and its intensity depend on the size of the stones, their type, number and location.

The main sign indicating the presence of stone-like structures is hepatic colic - a pain syndrome felt in the right hypochondrium and often radiating to the right shoulder blade, shoulder, lumbar region, and chest. Manifested due to the use of alcohol-containing drinks, high-fat foods. Often observed as a result of psycho-emotional or physical stress. The duration of the pain attack is 4-6 hours. The presence of stone-like formations is also indicated by symptoms:
- Vomiting containing bile.
- Intestinal disorders (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence).
- An increase in temperature to subfebrile indicators (37.1 - 37.8 degrees).
- Discoloration of feces.
- Increased fatigue, general weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Obstructive jaundice.
- Presence of a bitter taste in the mouth.
- The appearance of a white or brown coating on the surface of the tongue.
- The manifestation of pain during palpation of the cystic points.
- Detection of neutrophilic leukocytosis, eosinophilia.
- The manifestation of pain in the process of driving on uneven road surfaces.
- Individual intolerance to certain products.
Advanced cases are characterized by cholecystocardial syndrome, which manifests itself in the form of paroxysmal or aching pains localized in the region of the apex of the heart. Perhaps the appearance of pain in the joints, neurasthenic syndrome. With complete blockage of the ducts, fever, convulsive spasms, and increased sweating are observed.
Diagnosis of gallstone disease
To detect the disease, 2 types of methods are used - laboratory and instrumental. Laboratory studies include the collection of biochemical and general blood tests. In the presence of stones, there is an increase in the activity of aminotransferases, an increase in the level of leukocytes, bilirubin and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
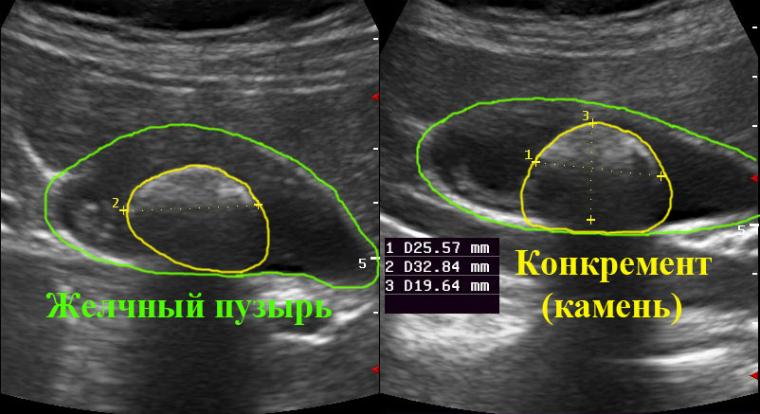
The main instrumental method is ultrasound, which allows to establish the state of the organs of the biliary system, the presence of inflammatory processes, as well as the exact localization of stones, their size and number. Additional diagnostics are possible in the following ways:
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography is a contrast antegrade examination of the biliary tract by blind percutaneous puncture of the liver.
- Endoscopic ultrasonography is an ultrasound study of pathology using a medical endoscope inserted inside through the esophagus. It is prescribed in the presence of obesity, flatulence.
- Cholecystocholangiography - the creation of an x-ray image of the ducts and bladder. Requires oral or intravenous administration of radiopaque iodine-containing compounds into the body. Used before laparoscopy.
- Radiography - obtaining an overview image of the upper abdominal cavity in order to detect calcifications.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is a method that requires the introduction of radiopaque substances into the ducts using an endoscope and provides for further examination of the biliary tract and bladder through an x-ray machine.
Detection of large stones is possible through palpation. Diagnosis and appointment of appropriate therapy is carried out by a gastroenterologist. If there are indications for surgical methods of treatment, a full-time consultation with a surgeon is required.
Types of stones in the gallbladder
Stones that form in the biliary system are divided into primary and secondary. The first type is formed in the cavity of the bladder for a long time due to changes in the structural composition of bile. Illness in this case does not show obvious symptoms.
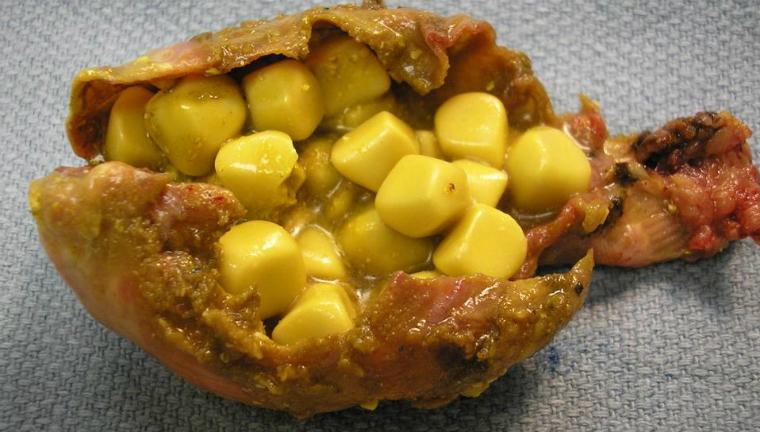

Secondary stones occur when there are violations of the outflow of bile: with cholestasis, biliary hypertension, as a result of clogging of the ducts by previously formed primary calculi. They can be localized in the bladder, ducts. In addition, stones are classified according to the following types:
- Lime. Appear with inflammatory phenomena that affect the walls of the gallbladder. Cholesterol crystals, pathogenic bacteria or scales of desquamated epithelium act as the core of this type of calculus.
- Cholesterol. Represented by rounded homogeneous structures, reaching 1.8 cm in diameter. Arise as a result of violations of metabolic reactions and are found in the cavity of the bladder in obese people.
- Bilirubin, or pigment. Like the previous species, they are non-infectious in nature. They are formed as a result of changes in blood proteins or in the presence of congenital pathologies that accelerate the destruction of red blood cells. These stones are localized in the cavity of the bladder, ducts and are characterized by small sizes.
- Concrements of mixed composition. They are formed on the basis of pigment or cholesterol stones due to the layering of calcifications on the main core. These processes occur against the background of the development of inflammatory phenomena.
The size of the stones can vary in a wide range - from 2 - 3 mm to 4 - 5 cm, the consistency - from waxy to solid, the configuration - from spherical to shapes irregular shape. The weight of one calculus is from 0.5 g to 80 g.
Treatment of gallstones without surgery
Conservative methods are effective in identifying initial stages ailment, in the presence of stony formations of small size (less than 1 cm in diameter). Such methods eliminate the need for surgical intervention, and make it possible to preserve the ducts and the organ itself.
What to do if stones are found in the gallbladder? It is possible to eliminate concretions by means of drug therapy, ultrasonic destruction of the nuclei of stones or alternative medicine methods. However, any chosen method of treatment should be carried out under strict medical supervision.
Dissolution of gallstones
To dissolve the formed stones, oral litholytic therapy is used, which involves the administration of drugs based on chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. Such drugs contribute to a change in the structural composition of bile: a decrease in cholesterol and an increase in the level of bile acids. Medical treatment is recommended under the following conditions:
- Preservation of normal contractility of the gallbladder in combination with good patency of the bile ducts.
- The predominance of cholesterol stones.
- The size of the stones does not exceed 1.5 cm, provided that they fill only half the volume of the bladder cavity.
- The possibility of taking drugs for a long period.
Duration of therapy - from six months to 2 years. Treatment should be accompanied by a refusal to use drugs that promote stone formation (antacids, cholestyramine, estrogens). The method is contraindicated for people with diseases of the digestive and urinary systems. The efficiency of removing stones by this method is 45 - 78%, the probability of recurrence in this case reaches 72%.
Crushing stones in the gallbladder
Mechanical destruction of stones is carried out by means of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. It is often used before the appointment of drug dissolution of stony formations. The principle of the method is based on the use of an ultrasonic wave, under the influence of which the calculi disintegrate into small fraction stones. A laser can be used for the same purpose. Indications for the procedure:
- No blockage of the bile ducts.
- Stone diameter less than 3 cm.
- The presence of stones of cholesterol origin without admixture of calcifications (up to 5 pieces).
Crushing is carried out in several stages: depending on the number and size of stones, 1-7 sessions are required, after which the removal of crushed stones occurs naturally through the biliary system. The procedure is prohibited for patients with bleeding disorders and people suffering from chronic diseases of the digestive tract. This is associated with the risk of blockage of the ducts and possible damage to the integrity of the walls of the main organ of the biliary system, which can cause inflammation and the formation of adhesions.
Folk remedies for removing stones from the gallbladder
Application of recipes traditional medicine requires mandatory medical consultation and is carried out only after determining the size of the calculi, their number and location using an ultrasound or x-ray examination. The following tools are well-deservedly popular:
- Sauerkraut juice. Used three times a day for 2 months. A single dose of a drink is 100 - 180 ml per dose.
- Rowan fruits. You should eat 250-300 g of fresh berries daily. The product can be eaten in combination with honey, bread, sugar. The duration of treatment is 1.5 months.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaves. 1 st. l. leaves are brewed with 180 - 200 ml of boiling water, kept for half an hour and filtered. A decoction is used up to 5 times a day at a dose of 2 tbsp. l. for the reception.
- Olive oil. It is taken orally on an empty stomach for 0.5 tsp. Gradually, a single dosage should be increased to 100 ml. Course duration - 3 weeks.
- Beet syrup. Fresh vegetables (3 - 5 pieces) are peeled and boiled for a long time until syrup is formed. The resulting liquid is used three times a day for 70 - 100 ml.
- Decoction of birch leaves. 1 st. l. dried vegetable raw materials pour 200 ml of boiling water and simmer for 20 minutes over moderate heat. The resulting extract is wrapped and infused for 1 hour, then filtered through a piece of gauze. The drug is taken on an empty stomach at a dose of 200 ml.
A prerequisite for the use of alternative medicine is the absence of allergic reactions to the components that make up the formulations. During the course of treatment, you need to pay attention to well-being. If the condition worsens, the medication should be discontinued.
Surgical treatment of gallstone disease
Treatment with surgical methods is recommended when large stones are found, frequent relapses of the disease, accompanied by fever, intense manifestations of pain, and the occurrence of various complications. The operation is performed by laparoscopic or open method.
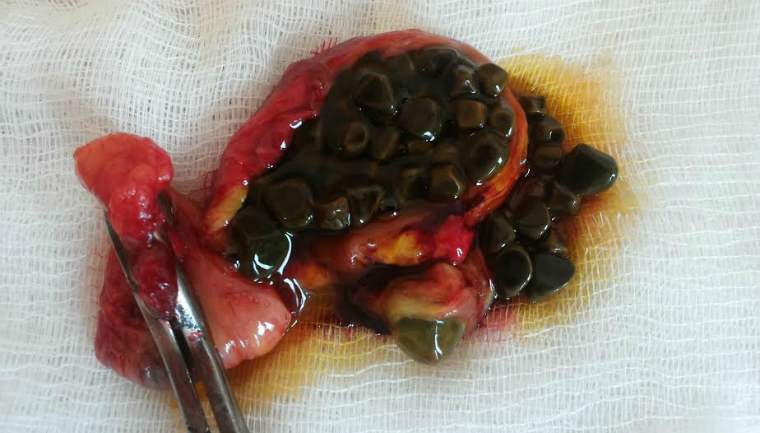
Removal of the gallbladder causes various diseases digestive system, which is associated with a deterioration in the digestibility of food. Therefore, surgical methods are resorted to in cases where conservative treatment has been ineffective. Surgical treatment options:
- Classical cholecystectomy - removal of the bladder with calculi through abdominal surgery. The main disadvantages of the technique are injury to a large area of healthy tissue when creating an incision (the length is from 15 to 20 cm) and a high risk of developing complications of varying severity.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy - removal of an organ using a specialized laparoscope apparatus, performed through small incisions (about 1 - 1.5 cm long). This method is considered sparing, as it helps to prevent the formation of noticeable scars and significantly shorten the rehabilitation period.
- Laparoscopic cholecystolithotomy is an organ-preserving surgical procedure that involves the extraction of formed stones.
Surgical treatment requires advance preparation of the patient: taking appropriate tests, considering possible risks, evaluating expected results to minimize possible complications. In case of deviations of analyzes from normal indicators, preliminary treatment is necessary in order to improve general condition.
Diet and nutrition for gallstones
Diet in the case of gallstone disease is of fundamental importance. In this case, fractional nutrition is recommended, which provides for eating at least 5 times a day, which stimulates the outflow of bile produced and prevents its stagnation.

The food consumed should contain the amount of animal proteins, vegetable fats, essential microelements (primarily magnesium) necessary for the body. Products that have a beneficial effect on the biliary system:
- Vegetables: carrots, cauliflower, pumpkin, zucchini.
- Meat and fish of low-fat varieties: beef, rabbit meat, veal, chicken, river fish.
- Dairy products with low fat content: milk, curd products, cheese, butter (as an additive to cereals).
- Cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, millet, semolina.
- Fruits and dried fruits: watermelon, apples, grapes, prunes.
- Juices, fruit drinks, compotes: quince, pomegranate, bird cherry, blueberry.
- Chicken eggs (if tolerated).
The diet should not include fatty foods and offal (meat, fish), canned food, spicy, sour, salty, fried foods, pastries from pastry, caffeinated and alcoholic drinks. In the presence of stones, vegetables with a high content of essential oils (turnip, garlic, radish, onion, radish) and oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel) should be strictly limited or excluded from the diet.
Possible complications of gallstone disease
The lack of timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment of cholelithiasis can cause the development of various complications (including severe diseases and their transition to a chronic form):
- Phlegmon of the bladder wall.
- Cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis (biliary form).
- Dropsy.
- Cholangitis.
- Empyema of the gallbladder and, as a result, its gangrene.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Oncological diseases of the biliary system.
- Bladder perforation.
- The formation of biliary fistulas.
- The occurrence of Mirizzi's syndrome.
- Rupture of the walls of the bladder with the subsequent development of peritonitis.
- Toxic hepatitis.
In the case of the development of one or another complication, the appointment of appropriate treatment is required, which is carried out in parallel with the treatment of gallstone disease. In severe cases, in the absence of adequate therapy, a lethal outcome is not excluded.
Prevention of the formation of stones in the gallbladder
The simplest and effective way prevention of the formation of stones is the observance of preventive measures. In this case, the main measures are healthy lifestyle life and the preparation of an optimal diet. In addition, tyubazh is useful, which can be carried out at home.

To prevent recurrence of the disease (re-formation of stones), it is recommended to continue oral litholytic therapy for a long period (up to 1 year). In addition, the following measures are effective:
- Refusal of food, characterized by a high content of cholesterol, animal fats, or severe restriction of the use of such products.
- In the presence of obesity, a gradual decrease in body weight to optimal parameters is recommended, which is possible through a low-calorie diet and regular exercise.
- Avoiding prolonged periods of fasting.
- Cessation of taking a number of drugs that contribute to the processes of stone formation (if any).
- The appointment of medications (Liobil, Zixorin), which reduce the body's production of cholesterol and stimulate the synthesis of bile acids.
Fractional nutrition, which involves the use of small portions every 3-4 hours, as well as the daily intake of vegetable fats (about 2 tsp of vegetable oil per day), significantly reduces the likelihood of stones in the biliary system and the development of concomitant diseases.
A bile stone of any size is an unpleasant phenomenon. For men and women, the causes of appearance are different, but for both sexes the statement is typical: the treatment of gallstone disease is a complex process, it is not always possible to do without surgery.
The reasons for the formation of stones or the occurrence of acute attacks with turn out to be different, each to a certain extent depends on the individual qualities of the patient, starting with the history of diseases, ending with genetics.
Among the most common reasons are:
- interruptions in food intake: first - overeating (the cause is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting), then, on the contrary, prolonged fasting;
- overweight problems, including obesity;
- sedentary work that does not allow movement during the working day;
- side effect of hormonal contraceptives;
- pathology of the pancreas.
The occurrence of stones in the ducts of the gallbladder is an unpleasant thing, unrecognized in time, provokes serious complications. For example, cholelithiasis can easily lead to biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
The composition of the stone stuck in the duct
By the nature of the pain, it is impossible to determine the composition of the stone that provoked cholelithiasis. , for example, often contain an admixture of calcium, not fully processed in the body, forced to be released in bypass ways.
Sometimes lime gets into the stones - a rather rare but well-known phenomenon. The presence of a substance in the stones is determined using the diagnostic method - cholecystography.
Stones in the liver ducts often appear as a parallel disease: the defeat of the first organ of the excretory system leads to the defeat of the second. Of course, the treatment of two diseases at the same time complicates the process, it is better to monitor the timely release of stones in advance, preventing the appearance of new ones.
Specific Symptoms
The first signs of gallstones in men and women are the same. In fact, already formed stones are able to stay in the ducts of the gallbladder for a long time, until a certain trigger mechanism causes the first symptoms of gallstone disease:
- the appearance of hepatic colic;
- the appearance of heaviness in the right side;
- bitter sensation in the mouth;
- belching, nausea, vomiting.
If the time of formation of gallstones is small, the first attack of exacerbation ends within 10-15 minutes, as the disease develops, an increase in the duration of the attack is also observed. If the pain does not go away within half an hour, it is better to call an ambulance, providing first aid.
General
Signs of gallstone disease are the same for men and women and include:
- the appearance of heaviness in the abdomen or on the sides;
- change in skin color: some patients turn pale, the integument of others turn yellow, darken;
- increased pain after eating (it is difficult for the digestive tract to cope with the load that has rolled in, there are difficulties in digestion);
- nausea accompanied by heartburn and vomiting;
- change in stool, discharge - profuse diarrhea or persistent constipation;
- if already digested food returns to the stomach, belching, heartburn, increased gas formation, and in some cases, vomiting may occur.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of the symptoms, the duration of the attacks, in which the patient feels worse, differ.
Typically masculine
Men suffer from gallbladder diseases 2 times less often than the opposite sex - the frequency is associated with a different system of the biological structure of the body, including the production of hormones. The symptoms of gallstone disease in men do not differ from the general classification, in women certain nuances are known.
Typically feminine
It is believed that gallstone disease is more common in older women, especially those who are overweight. The symptoms of gallstones in women are different from those of the opposite sex. Pathology is indeed observed in older women, but the change in the body under the influence of the fetus plays a significant role.

If a girl before pregnancy had a predisposition to the occurrence of a disease, difficulties with the functioning of the liver, problems with the excretion of bile are quite likely to occur. The occurrence of a disease during pregnancy is more dangerous, it is better to think about timely diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of "cholelithiasis" is made on the basis of the symptoms listed by the patient to the attending physician at the first appointment. A number of procedures are known that are mandatory for diagnosis, helping to confirm or refute the diagnosis:
- complete blood count (establishes the clinical stage of the disease, the presence of inflammation);
- biochemical blood test (with stones in the liver - the activity of substances directly involved in metabolism is detected);
- cholecystography (helps to determine whether the organ has increased in size);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (the most accurate analysis that allows you to determine the presence and size of stones, possible blockage of the ducts, cholecystitis is diagnosed and pathological complications are identified).
Only after establishing the correct diagnosis is it permissible to begin treatment.
Treatment of gallstone disease
If the bile ducts are not able to clear themselves due to the inactivity of the patient, it makes sense to prescribe a targeted treatment for gallstone disease. The main methods of dealing with stones in the ducts of the gallbladder include:

- Compliance with a special diet.
- Taking special preparations that allow you to dissolve stones directly in the internal organ. The drugs are harmless, apart from possible side effects due to contraindications: the dissolved substances simply remain in the gallbladder or are excreted along with the bile. There is no stone that hinders the removal of bile, it is easier for the bile ducts to function. The disadvantages of such treatment include the ability to dissolve only stones of small size, not exceeding 1 cm, and the method does not stop the process of formation of calculi. After a year and a half of treatment, the stones reappear.
- Lithotripsy is the destruction of stones in an alternative way: with the help of a strong shock wave created by special devices. It is used against accumulations of cholesterol, in a size not exceeding 3 centimeters. The number of destroyed accumulations at a time is three, if there are more stones in the ducts, another method is assigned. Thanks to such a forceful impact, accumulations of substances begin to break up into small grains that pass through the ducts with greater ease, excreted from the body in a completely natural way: urine and feces. The method does not cause pain, is carried out without hospitalization of the patient.
If the therapeutic course does not help, we are talking about surgery. It will not work otherwise to free the ducts from excess substances and formations. In selected cases, it is necessary to remove the gallbladder, it becomes obviously clear that it is better to forget about the normal functioning of the organ.
Treatment goals include:
- cleansing of the bile ducts;
- return of normal liver function;
- normalization of bile production in the body.
If, at the end of the course, the patient can safely say that digestion has improved, most of the unpleasant symptoms have disappeared, then the treatment has been successful. However, a weakened body needs reverent care, certain preventive measures must be observed. The postoperative regimen is prescribed by the doctor, according to the patient's medical history, there are also common features.
Preventive measures
After completion of treatment, preventing exacerbations, a special diet is prescribed, the products of which have a positive effect on the gallbladder and gastrointestinal tract, without creating an excessive load. With gallstones, a high risk of recurrence of deposits, a person's diet plays a huge role. The condition of the patient depends on the type of food eaten.
Gallstone disease is an unpleasant disease, but the disease will recede if you start fighting in time and stop the subsequent occurrence of stones in the bile and hepatic ducts.
The number and size of gallstones are very diverse: sometimes it is one large stone, but more often - multiple stones, numbering in tens, sometimes hundreds. They range in size from a chicken egg to millet grain and less. Stones may vary in chemical composition. Cholesterol, lime and bile pigments are involved in their formation. Consequently, metabolic disorders in the body, bile stasis and infection play an important role in the process of stone formation. When bile stagnates, its concentration increases, conditions are created for the crystallization of cholesterol contained in it and excreted from the body with it. It has been scientifically established that excessive and irregular nutrition, as well as insufficient mobility, contribute to the creation of conditions for the formation of gallstones. The most common causes of biliary colic (the main manifestation of cholelithiasis) are the use of alcohol, spicy fatty foods, excessive exercise.
A common metabolic disease in which, due to a violation of the processes of bile formation and bile secretion, the formation of stones in the gallbladder occurs. Small stones (microliths) are sometimes also formed in the intrahepatic bile ducts, especially in older men and patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Once in the gallbladder, microliths can serve as a basis for cholesterol to settle on them and form large cholesterol stones. In addition to cholesterol stones, there are pigmented (bilirubin), calcareous, mixed and combined types of stones. Stone carrying is possible without clinical manifestations; often it is accidentally discovered at autopsy. Gallstones occur at any age, and the older the patient, the higher the frequency of the disease. In women, gallstone disease and stone carrying are observed several times more often than in men.
Cholelithiasis is often accompanied by chronic cholecystitis. With multiple stones, bedsores form in the gallbladder, which can lead to ulceration and perforation of its walls.
Classification
- In cholelithiasis, stages are distinguished: physicochemical (changes in bile), latent (asymptomatic stone-carrying), clinical (calculous cholecystitis, biliary colic).
- There are the following clinical forms of cholelithiasis: asymptomatic stone carrying, calculous cholecystitis, biliary colic.
- Gallstone disease can be complicated and uncomplicated.
The main manifestation of cholelithiasis is biliary, or hepatic, colic, which is manifested by bouts of very severe pain in the right hypochondrium. At the same time, they spread and give to the right shoulder, arm, collarbone and shoulder blade or to the lower back with right side body. The most severe pain occurs when the blockage of the common bile duct occurs suddenly.
An attack of biliary colic is accompanied by nausea and repeated vomiting with an admixture of bile in the vomit, which does not alleviate the condition of patients. Sometimes there are reflex pains in the region of the heart. Biliary colic usually occurs with an increase in body temperature, which lasts from several hours to 1 day.
Between attacks, patients feel practically healthy, sometimes they feel dull pains, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, and nausea. There may be a decrease in appetite, dyspeptic disorders.
With prolonged blockage of the common bile duct, bile from the liver is absorbed into the blood, jaundice occurs, which requires appropriate treatment in a hospital setting.
The most reliable confirmation of the diagnosis of gallstone disease is the results of an X-ray examination with the introduction of a radiopaque fluid into the bile ducts.
In the clinical manifestations of cholelithiasis, functional disorders of the extrahepatic biliary tract are essential both in the early period before the formation of stones, and in the presence of such. Gallstone disease is quite common, especially in women, a disease accompanied by a number of complications and successive processes.
The size and number of gallstones fluctuate in different cases. The most voluminous are single, solitary stones (monoliths), and the weight of the stone can reach 25-30 g; Gallbladder stones are usually round, ovoid in shape, common bile duct stones resemble the end of a cigar, and intrahepatic duct stones may be branched. Small stones, almost grains of sand, may be among the several thousand in one patient.
The main components of the stones are cholesterol, pigments (bilirubin and its oxidation products) and lime salts. All these substances can be combined in various proportions. From organic substances, they contain a special colloidal substance of a protein nature, which forms the skeleton of a stone, and from inorganic, in addition to lime salts (carbonic and phosphate), iron, copper, magnesium, aluminum and sulfur were found in gallstones. For practical purposes, it is enough to distinguish three types of stones according to their chemical composition: cholesterol, mixed and pigmented.
- Cholesterol, radiar stones consist almost exclusively (up to 98%) of cholesterol; they are white, sometimes slightly yellowish in color, round or oval in shape, ranging in size from a pea to a large cherry.
- Mixed stones, cholesterol-pigment-lime, multiple, faceted, found in tens, hundreds, even thousands. These are the most common, most common stones. On the cut, one can clearly see a layered structure with a central core, which is a soft black substance consisting of cholesterol. In the center of mixed stones, fragments of the epithelium, foreign bodies (blood clot, dried roundworm, etc.) are sometimes found, around which stones falling out of bile are layered.
- Pure pigment stones are of two types: a) observed in cholelithiasis, possibly with plant nutrition, and b) observed in hemolytic jaundice. These pure pigment stones are usually multiple, black in color, turn green when exposed to air; they are found in the bile ducts and in the gallbladder.
Causes of gallstone disease (stones in the gallbladder)
The development of gallstone disease is a complex process associated with metabolic disorders, infection and bile stasis. Undoubtedly, heredity also matters. Metabolic disorders contribute to the violation of bile eicolloidality. The stability of the bile colloidal system, its surface activity and solubility depend on the composition and correct ratio of bile ingredients, primarily bile acids and cholesterol (the so-called cholate-cholesterol index). An increase in the concentration of cholesterol or bilirubin in bile can contribute to their loss from solution. The prerequisites for increasing the concentration of cholesterol and reducing the content of cholates in bile are created during stagnation of bile. The infection promotes stone formation by inhibiting the synthesis of bile acids by the liver cells. All these mechanisms, closely related to each other, lead to the development of the disease, which is facilitated by neuro-endocrine and metabolic disorders. Hence the more frequent development of cholelithiasis among people with obesity, an unhealthy lifestyle, its frequent association with other metabolic diseases (atherosclerosis, diabetes), as well as the frequent occurrence of the disease during repeated pregnancy.
Great importance in the formation of gallstones has, apparently, an abnormal composition of bile produced by the liver (dyscholia), which contributes to the precipitation of sparingly soluble constituent parts bile, as well as a violation of the general metabolism with an overload of blood with cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) and other products of slow metabolism. Infection leading to disruption of the integrity of the epithelium of the gallbladder mucosa with its desquamation, foreign bodies inside the gallbladder, easily causing the deposition of lime and other components of bile, are rather only secondary, more rare factors in stone formation. Excessive bile secretion of bilirubin in massive hemolysis is of the same importance.
At the heart of violations of the liver and changes in metabolism are the adverse effects of the external environment in the form of excessive malnutrition, lack of physical work. Of great importance are the neuroendocrine factors that affect the function of the liver cell and tissue metabolism, as well as the emptying of the gallbladder.
Gallstone disease is often combined with obesity, gout, the presence of kidney stones, sand in the urine, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, that is, it is observed in numerous conditions that occur: with hypercholesterolemia.
The disease most often manifests itself between the ages of 30 and 55, and women are 4-5 times more likely than men. Gallstones with inflammation of the gallbladder and hemolytic jaundice can be observed at an earlier age. Cholelithiasis, of course, often manifests itself clinically for the first time during pregnancy or in the postpartum period: pregnancy is accompanied, under normal conditions, by physiological hypercholesterolemia and increased liver cell function, which creates the best conditions for fetal development and milk production by the mammary gland. Particularly significant disturbances of metabolic and vegetative processes can be expected in violation of the physiological rhythm of the function of childbearing during repeated abortions or premature births without subsequent lactation, etc., when a delay in the emptying of the gallbladder is also possible due to altered activity of the nervous system. Family cases of gallstone disease, especially frequent in mother and daughter, are most often explained by the influence of the same environmental conditions mentioned above.
It has long been known that foods rich in cholesterol (fatty fish or meat, caviar, brains, butter, sour cream, eggs) contribute to the formation of stones, of course, in violation of oxidative-enzymatic processes.
Experimental studies of recent times have also found the effect of vitamin A deficiency on the integrity of the epithelium of the gallbladder mucosa; its desquamation contributes to the precipitation of salt and other precipitation.
Currently, great importance in the loss of cholesterol in bile is attached, as indicated, to the abnormal chemical composition of bile, in particular, the lack of bile (and also fatty) acids, which can be seen as a violation of the function of the liver cell itself.
Known value in cholelithiasis have infections and stagnation of bile. Of the transferred diseases, special attention was paid to typhoid fever, since it is known that typhoid bacillus can affect the biliary tract, excreted with bile.
Stagnation of bile contributes, in addition to a sedentary lifestyle, excessive fullness, pregnancy, clothing that squeezes the liver or restricts the movement of the diaphragm, prolapse of the abdominal organs, mainly the right kidney and liver; at the same time, an inflection of the bile ducts, especially the cystic one, located in the lig. hepato-duodenale. With swelling of the duodenal mucosa and scarring of ulcerative processes in it, the mouth of the common bile duct can be compressed, which leads to stagnation of bile. Catarrh resulting from a gross violation of the diet sometimes contributes to stagnation of bile and infection of the biliary tract. Usually, however, in addition to the mechanical factor, the action of the above liver-exchange factor is also noted.
The greatest importance in the origin of cholelithiasis should be given to a violation of the nervous regulation of various aspects of the activity of the liver and biliary tract, including the gallbladder, with their complex innervation device. The formation of bile, its entry into the gallbladder and its release into the duodenum is finely regulated by autonomic nerves, as well as by higher nervous activity, for which the great importance of conditioned reflex connections for normal bile secretion speaks.
At the same time, the receptor fields of the biliary tract, already with functional disorders of the biliary function, give rise to pathological signaling to the cerebral cortex. Thus, in the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis, it is possible to establish individual links that are also characteristic of other cortical-visceral diseases.
Exchange-endocrine disorders play only a secondary role, subject to functional changes in the nervous regulation. With an initial lesion of adjacent organs and infectious causes, a violation of the activity of the hepatic-biliary system, leading to cholelithiasis, also occurs in a neuroreflex way.
Separate signs of gallstone disease, especially the signs accompanying biliary colic, characteristic of gallstone dyspepsia, etc., owe their intensity and variety, primarily to the abundant innervation of the gallbladder and biliary tract, and are undoubtedly mainly neuroreflex in nature.
Symptoms, signs of gallstone disease (stones in the gallbladder)
The clinical picture of gallstone disease is extremely diverse and difficult to brief description. Uncomplicated cholelithiasis is manifested by cholelithiasis dyspepsia and biliary, or hepatic, colic.
Complications of gallstone disease
- biliary colic.
- Cholecystitis.
- Acute pancreatitis.
- Fistula of the gallbladder, mechanical intestinal obstruction.
- Obstructive jaundice.
- Cholangitis and septicemia or liver abscess.
- perforation and peritonitis.
Cholelithiasis is characterized by a chronic course, leading to disability of patients and even threatening their lives during certain periods of the disease in the presence of certain complications, especially as a result of blockage of the biliary tract, intestinal obstruction and phlegmonous cholecystitis. Often, the disease takes a latent (latent) course, and stones are found only at the autopsy of patients who died from another cause.
Of the complications of cholelithiasis, almost as numerous as, for example, complications of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, obstruction of the biliary tract and their infection are described primarily separately, although very often the phenomena of obstruction and infection are combined.
Stones can get stuck in their movement at various points along the path of bile flow, causing special characteristic clinical symptoms. Most often it is necessary to observe blockage of the cystic and common bile duct.
A typical manifestation of the disease is an attack of biliary, or hepatic, colic. The pains come on suddenly, but sometimes they are preceded by nausea. Colic usually begins at night, more often 3-4 hours after an evening meal, especially fatty foods, drinking alcohol; accompanied by a rise in temperature (sometimes with chills), tension in the abdominal muscles, stool retention, bradycardia, vomiting, and bloating. Possible temporary anuria, in the presence of coronary disease - the resumption of anginal attacks. In the duodenal contents, a large number of cholesterol crystals, sometimes small stones are found. In some cases, stones can be found in the stool 2-3 days after the attack. In some cases, colic is repeated often, in others - rarely, proceeding in the form of gallstone dyspepsia.
With biliary colic, complications are possible, of which the most dangerous is blockage of the neck of the gallbladder with a stone; as a result of laying an artificial path to the intestine (fistula) with a stone, a severe infection of the biliary apparatus occurs with the development of abscesses, biliary peritonitis and sepsis in it. Gallstone disease favors the development of malignant neoplasms of the biliary system.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of cholelithiasis (gallstones)
The diagnosis of cholelithiasis is made on the basis of complaints of patients, anamnesis and the course of the disease. In the anamnesis, indications of the dependence of complaints on fatty and starchy foods, their connection with pregnancy, the fullness of patients (in the past), the presence of cases of cholelithiasis in the family (in the mother of the patient, sisters) under the same external living conditions are especially important.
When examining patients, the possibility of gallstone disease is indicated by the presence of at least slight jaundice, skin pigmentation (liver spots, chloasma), cholesterol deposition in the skin (cholesterol nodes - xanthelasma - in the thickness of the eyelids near the nose). Often, patients have overdeveloped subcutaneous fat. However, cholelithiasis affects, especially in connection with an infection of the biliary tract, also persons with normal and underweight. As a result of the severe course of cholelithiasis, its complications, patients can lose weight dramatically, even acquire a cachectic appearance. The content of cholesterol in the blood may fall below the norm, although often cholelithiasis is accompanied by elevated levels of blood cholesterol. Direct evidence of the presence of a stone can be given by cholecystography, the results of which are positive with modern technology in 90% of patients; detection of microliths in duodenal contents also matters.
As for the differential diagnosis, in various stages of cholelithiasis one has to keep in mind a number of diseases. With gallstone dyspepsia, it is necessary to exclude, first of all, gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic appendicitis, colitis and many other causes of gastric and intestinal dyspepsia. Erased signs of gallstone dyspepsia, described in detail above, allow clinically clarifying the diagnosis.
Hepatic colic has to be differentiated from a number of diseases.
- With renal colic, pain is localized below, in the lumbar region, and radiates to the groin, genitals and leg; often there is dysuria, anuria, blood in the urine, and sometimes sand; the vomiting is not so persistent, the febrile reaction is less common. We must not forget that both colic can be observed simultaneously.
- With food poisoning, the manifestations begin suddenly with profuse food vomiting, often diarrhea, in the form of an outbreak of a number of diseases, there is no characteristic dyspepsia in the anamnesis.
- In acute appendicitis, pain and tension of the abdominal wall (muscular protection) are localized below the navel, the pulse is more frequent, etc.
- Duodenal ulcers and periduodenitis, due to their anatomical proximity to the gallbladder, are especially often mixed with biliary colic. A detailed analysis of the pain syndrome, pain points and x-ray examination helps to establish the diagnosis.
- Myocardial infarction can give a similar picture, especially since pain and infarction can only be localized in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen (“status gastralgicus” due to acute congestive liver). The history of patients, electrocardiographic changes, etc., resolve the issue. Angina pectoris and even myocardial infarction can be caused by biliary colic. Nitroglycerin, according to some authors, also facilitates an attack of gallstone disease.
- Acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis is characterized by more pronounced general phenomena (see when describing this form).
- Intestinal colic is characterized by periodic pain with rumbling and is sometimes accompanied by diarrhea.
- Mesenteric lymphadenitis (usually tuberculous) when located in the right upper quadrant is sometimes accompanied by pericholecystitis and periduodenitis without affecting the gallbladder itself, but is often mistakenly recognized as chronic cholecystitis.
- Tabetic crises give less intense pain, vomiting with them is more abundant, the temperature is not elevated, there are neurological signs of dorsal tabes.
- With lead colic, the pains are localized in the middle of the abdomen, they are spilled, they calm down with deep pressure; the abdomen is usually retracted and tense; blood pressure is increased; the gums have a typical lead border.
As stated above, biliary colic is almost always caused by stones, but in rare cases, it can be caused by ascaris stuck in the ducts or echinococcus bladder. The analysis of feces and the presence of other symptoms of ascaris invasion or echinococcal disease helps to establish the diagnosis.
Enlarged gallbladder with dropsy, it can be mixed with hydronephrosis, pancreatic cyst; the gallbladder is characterized by respiratory mobility and lateral displacement; the anterior echinococcal cyst of the liver is differentiated from hydrocele of the bladder according to the rest of the signs characteristic of echinococcal disease.
It is necessary to differentiate febrile cholecystitis, obstructive stone jaundice, pseudomalarial cholangitis fever, secondary biliary cirrhosis of the liver, gallstone ileus, etc. from other diseases that may resemble the corresponding complication of cholelithiasis along the course.
Forecast and working capacity of cholelithiasis (stones in the gallbladder)
The prognosis of cholelithiasis is difficult to formulate in a general form, the course of the disease is so diverse. In most cases, the disease proceeds with recurrent pain attacks and dyspepsia and, with the right regimen, is not prone to progression and does not significantly shorten life expectancy. Such is the course of cholelithiasis in most sanatorium-and-spa patients. In patients in the therapeutic departments of hospitals, a more persistent course with complications is usually observed; finally, in patients with surgical departments, the most serious complications of cholelithiasis are noted, giving a relatively high mortality rate.
With frequent exacerbations of cholelithiasis and severe inflammatory phenomena (fever, leukocytosis), which are not inferior to treatment, patients are completely disabled or their ability to work is limited. In milder cases of cholelithiasis with a predominance of spastic or dyskinetic phenomena in the gallbladder area, without pronounced symptoms of cholecystitis, patients should be recognized as limited able-bodied in the presence of significant severity and persistence of nervous disorders and frequent, mostly non-infectious, subfebrile condition. They cannot perform work associated with significant physical stress. With the development of severe complications of cholelithiasis, patients are completely disabled.
Prevention and treatment of gallstone disease (stones in the gallbladder)
To relieve a painful attack intravenously, intramuscularly, antispasmodics (drotaverine hydrochloride, papaverine hydrochloride) and analgesics (metamisole sodium, promedol) are administered. If it is still not possible to eliminate the attack and the jaundice does not go away, one has to resort to surgical treatment. To remove stones, lithotripsy is used - their crushing with the help of a shock wave.
Patients with gallstone disease must strictly observe the diet and diet, do not abuse alcohol.
Patients with chronic diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract with insufficient bile secretion and a tendency to constipation are recommended a diet with a high content of magnesium, calcium, carotene, vitamins B, A. If bile enters the intestine in insufficient quantities, then you should limit the consumption of animal fats. It is also recommended to consume more honey, fruits, berries, raisins, dried apricots.
To prevent the development of the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the gallbladder, timely treatment of infectious diseases is necessary. In cases where cholelithiasis is combined with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder (chronic cholecystitis), the disease is much more severe. Attacks of biliary colic are more frequent, and most importantly, severe complications (hydrops of the gallbladder, cholangitis, pancreatitis, etc.) can develop, the treatment of which is very difficult.
For the prevention of gallstone disease, a hygienic general regimen, sufficient physical activity and proper nutrition, as well as the fight against infections, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, elimination of bile stasis, and elimination of nervous shocks are important. For people leading a sedentary lifestyle, it is especially important to avoid overeating, systematically take walks in the fresh air, and play light sports.
Treatment of gallstone disease at various stages of its development is not the same. However, regardless of temporary urgent measures, patients, as a rule, must observe a general and dietary regimen for years and decades, periodically undergo spa treatment in order to counteract metabolic disorders, cholesterolemia, to increase the activity of liver cells, to strengthen the nervous regulation of bile-hepatic activity. Of great importance is the fight against stagnation of bile, infection of the gallbladder and biliary tract, ascending from the intestine or metastasizing from distant foci, as well as eliminating difficult experiences. It is necessary to recommend fractional nutrition (more often and little by little), as it is the best choleretic agent. The daily amount of drinking should be plentiful to increase secretion and dilute bile. It is important to eliminate all causes that contribute to the stagnation of bile (for example, a tight belt); with severe ptosis, wearing a bandage is necessary. Constipation should be controlled by diet, enemas, and mild laxatives.
Dietary nutrition is very important in the treatment of gallstone disease. In acute attacks of biliary colic, a strict sparing regimen is necessary. Concomitant lesions of the gastrointestinal tract or other diseases (colitis, constipation, diabetes, gout) should be taken into account.
In cholelithiasis, it is usually necessary to limit patients both in terms of total caloric intake of food, and in relation to meat, fatty dishes, especially smoked foods, canned food, snacks, and alcoholic beverages. Egg yolks and brains, especially rich in cholesterol, should be excluded from food, and butter should be sharply limited. . The diet should be predominantly vegetarian with a sufficient amount of vitamins, for example, vitamin A, the lack of which in the experiment leads to a violation of the integrity of the epithelium of the mucous membranes and, in particular, to the formation of gallstones. Much attention is paid to the culinary processing of food, and fried meat, strong sauces, broths, and some seasonings should be avoided. It is necessary to take into account not only the physicochemical properties of food, but also its individual tolerance.
During the period of sharp exacerbations of the disease, a meager diet is prescribed: tea, rice and semolina porridge on the water, kissels, white unbread crackers. Only gradually add fruits (lemon, applesauce, compotes), cauliflower, other mashed vegetables, a little milk with tea or coffee, yogurt, low-fat broth or vegetable soup, etc. From fats, fresh butter is allowed in the future in a small amount , with breadcrumbs or vegetable puree; Provence oil is given as a medicine with tablespoons on an empty stomach. Patients for years should avoid those dishes that cause them attacks of colic or dyspepsia, namely: pies, cream cakes and pastry in general, saltwort, pork, fatty fish, cold fatty snacks, especially with alcoholic drinks, etc. .
The regimen of patients with cholelithiasis should not, however, be limited only to a properly selected diet and rational eating habits; patients must avoid excitement, hypothermia, constipation, etc., in a word, all those irritations which, according to their experience, lead with particular constancy to the return of colic, to a large extent, probably due to the zones of prolonged excitation created in the cerebral cortex. Taking drugs that strengthen the inhibitory process in higher nervous activity, distraction, and similar other methods should be used to prevent another attack even when exposed to the usual provoking factors.
In the treatment of cholelithiasis, one of the first places is occupied by sanatorium treatment, which is indicated after the passage of acute attacks (not earlier than 1-2 months) for most patients with uncomplicated cholelithiasis without signs of a pronounced decline in nutrition. Patients are sent mainly to Zheleznovodsk, Essentuki, Borjomi, etc. or to sanatoriums at the place of residence of patients for dietary and physiotherapy. In sanatorium treatment, complete rest, proper general regimen, nutrition, measured walks, topical application of mud to the liver area, which relieves pain and accelerates the cure of residual inflammatory processes, and drinking mineral waters are beneficial. Of the mineral waters, hot bicarbonate-sulphate-sodium (for example, the Zheleznovodsk Slavyanovsky spring with water at a temperature of 55 °), hydrocarbonate-sodium sources of Borjomi and others are used, which contribute to a better separation of more liquid bile and the cure of gastrointestinal catarrhs, as well as better loosening the intestines and diverting blood from the liver. Mineral or salt-coniferous baths are also used, which act favorably on the nervous system.
Under the influence of climate, mineral waters, hydrotherapy procedures, topical application of mud and, finally, an appropriate dietary regimen, the metabolism changes in a favorable direction, inflammation subsides, bile becomes less viscous and is easier to remove from the biliary tract, and normal nervous regulation is largely restored. activity of the hepatobiliary system.
Of the medicines, bile acids (decholine) can be important, which make it possible to ensure a normal ratio of bile acids and cholesterol and thereby counteract stone formation; herbal preparations rich in anti-spasmodic, anti-inflammatory, laxative ingredients; preparations from plants with choleretic properties (holosas extract from rosehip berries, infusion of sandy immortelle-Helichrysum arenarium and many others), choleretic and laxative salts - magnesium sulfate, artificial Carlsbad salt, etc.
Treatment of biliary colic consists in the vigorous application of heat to the area of the liver in the form of heating pads or compresses; if the patient does not tolerate heat, ice is sometimes applied. Assign painkillers: belladonna, morphine. Usually vomiting does not allow oral medication, and most often it is necessary to inject 0.01 or 0.015 morphine under the skin, preferably with the addition of 0.5 or 1 mg of atropine, since morphine, apparently, can increase spasms of the sphincter of Oddi and thereby increase blood pressure. bile ducts.
Novocaine also relieves colic (intravenous administration of 5 ml of a 0.5% solution), papaverine. Many patients experience bloating during an attack; in these cases, warm enemas are prescribed; with persistent constipation, siphon enemas are used. Vomiting can be soothed by drinking hot black coffee or by swallowing pieces of ice.
Within 5-6 days after the attack, it is necessary to monitor whether the stone is excreted in the stool. In the prevention of a seizure, rest, the prohibition of bumpy driving, an appropriate diet with restriction of fatty and spicy foods, fractional nutrition with sufficient fluid intake and elimination of constipation are important.
In case of infection of the biliary tract, sulfazin and other sulfonamide drugs are used in an average dose, penicillin (200,000-400,000 units per day), hexamine, "non-surgical drainage" of the biliary tract in combination with agents that increase the body's resistance and improve the condition of the liver: intravenous infusion of glucose, ascorbic acid, campolone, blood transfusion, etc.
With obstructive jaundice, the same drugs are prescribed that improve the condition of the liver, and in addition, ox bile, vitamin K inside parenterally (against hemorrhagic diathesis).
Urgent surgical treatment is indicated for gangrenous cholecystitis, perforated peritonitis, intestinal obstruction on the basis of a stone (simultaneously with treatment with penicillin). Surgical intervention is subject to limited accumulations of pus with empyema of the gallbladder, subdiaphragmatic abscess, purulent cholecystitis, blockage of the common bile duct by a stone, dropsy of the gallbladder, purulent cholangitis. More often, an operation is performed to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) or to open and drain the gallbladder or common bile duct. After the operation, the correct general and dietary regimen is also necessary in order to avoid recurrence of stone formation or inflammatory-dyskinetic phenomena, as well as spa treatment.
In some cases, it should be only conservative, in others, it must be surgical. Foods rich in cholesterol and fats (brains, eggs, fatty meats), rich meat soups, spicy and fatty foods, lard, smoked meats, canned food, rich confectionery, alcoholic beverages should be excluded from nutrition. Dairy products, fruit and vegetable juices, vegetables, vegetarian soups, boiled meat, fish and pasta, cereals, berries, butter and vegetable oil, preferably corn. It is necessary to advise patients to eat moderately, regularly and often, with plenty of drink, giving preference to mineral waters (Essentuki No. 20, Borzhom, etc.).
Assign various choleretic drugs. Karlovy Vary salt, magnesium sulfate, sodium sulfate, allochol, cholecine, cholenzim, oxafenamide, cholagol, flamin, cholelitin, etc. are very effective. colic sometimes it is necessary to prescribe pantopon or morphine, always with atropine, since morphine preparations can cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. In the presence of symptoms of an "acute abdomen", the use of drugs is contraindicated.
In the presence of infection, antibiotics are used, taking into account the sensitivity of the flora isolated from bile, for 5-10 days; sulfa drugs.
Surgical treatment is carried out in cases of a persistent course of the disease, with frequent relapses of biliary colic that occur despite active treatment, with blockage of the gallbladder, perforation of the bladder, and the formation of biliary fistulas. Operative treatment of cholelithiasis should be timely.
stonesin the gallbladder- These are fairly solid, dense formations. Quantity stones in the gallbladder can be different - from one to many hundreds and even thousands. The size of the stones is also different - from a grain of sand and a pinhead to a plum and a chicken egg. The more stones in the gallbladder, the smaller they are. Most often stones located in the gallbladder, less often - in the bile and hepatic ducts, in the intrahepatic bile ducts.
The reasons
- pregnancy;
- irregular meals or very rare meals;
- eating fatty foods;
- congenital hemolytic anemia;
- hypovitaminosis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive body weight;
- heredity and family traditions burdened with metabolic disorders;
- typhoid fever or salmonellosis in history;
- transferred malaria;
- eating fatty foods;
- viral hepatitis;
- diabetes;
- constipation;
- wearing tight belts;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- the use of estrogenic contraceptives and anti-atherosclerotic drugs;
- chronic violation of duodenal patency.
Availability stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts and
gallstone disease.
Biliary dyskinesia, gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, colitis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract contribute to the disease, but cholecystitis is especially dangerous in this regard - inflammation of the gallbladder.
Symptoms
For cholelithiasis characterized by intense paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the right shoulder blade, shoulder, neck, accompanied by vomiting, bitterness, dry mouth, skin itching, fever. Jaundice may develop. Palpation reveals pain in the right hypochondrium in the projection of the gallbladder.
Clinical forms
According to the nature of the course of the disease, latent, dyspeptic, painful paroxysmal and painful torpid forms.
1. Latent form of gallstone disease often observed in the presence of single, usually cholesterol stones. Patients feel normal, the presence of stones is determined by chance during ultrasound. The latent form of gallstone disease is more common in older people and men.
2.Dyspeptic form of gallstone disease observed in about 1/3 of cases of cholelithiasis. For many years, patients may experience periodic or persistent nausea, heaviness after eating, belching, bitterness in the mouth, dyspeptic disorders, which are usually associated with the use of fatty, fried or spicy foods, carbonated drinks. Local symptoms of gallbladder damage are mild or completely absent for a long time. Very often, all these manifestations are attributed to dysbacteriosis, and most often it is really present, but as a secondary pathology.
3. Painful paroxysmal form of gallstone disease- the most common and easily diagnosed. It is characterized by a recurrent course: severe pain attacks occur unexpectedly and for no apparent reason or after malnutrition, physical stress, etc.
4. Painful torpid form of gallstone disease characterized by the absence or rarity of seizures. The pain is dull, constant or intermittent. Under the influence of dietary disorders, physical stress, the pain intensifies, but does not reach the severity of typical colic. Increased pain in most cases is short-lived. During an exacerbation, there is no increase in body temperature, the level of leukocytes in the blood and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate remain normal.
According to the severity of the clinical course, 3 forms of gallstone disease.
1. Light form cholelithiasis is characterized by rare attacks of biliary colic (from 1 to 5 times a year) lasting from 30 minutes to 1 hour (rarely more), short-term fever without jaundice while maintaining the concentration and motor functions of the gallbladder. Attacks are easily removed by medication. In the period between attacks, pain syndrome and dyspeptic symptoms are poorly expressed.
2. Moderate form cholelithiasis is characterized by a moderately pronounced persistent pain syndrome and periodic attacks of biliary colic. Attacks occur 6-12 times a year lasting 3-6 hours or more, accompanied by fever, recurrent vomiting, often jaundice. Fever, icteric staining of the sclera persist for 2-3 days after the attack. Significant changes in the biliary tract (cholangitis) and liver (hepatitis) are accompanied by symptoms of secondary pancreatitis. In the period between attacks, a moderately pronounced persistent pain syndrome and dyspeptic symptoms persist. Perhaps a violation of concentration (the ability to make bile more concentrated, which allows the liver to produce it smoothly) and motor functions of the gallbladder, a moderate change in liver function, exocrine function of the pancreas.
3. Severe form cholelithiasis is characterized by frequent (2-3 times a week) and prolonged attacks of biliary colic. Attacks are removed only by repeated use of strong painkillers. In the period between attacks, there is a pronounced persistent pain syndrome, dyspeptic disorders, subfebrile temperature. Violated concentration and motor functions of the gallbladder, liver function and exocrine function of the pancreas.
Diagnostics
To identify cholelithiasis there are many reliable ways. But the main remains analysis of the general condition of a person.
Experienced gastroenterologist already with a careful examination, he can determine how big the problems of his patient are: whether the gallbladder is enlarged, the degree of its sensitivity, etc. But, of course, only a thorough analysis of the entire set of clinical symptoms and the results of auxiliary research methods makes it possible to make a correct diagnosis.
For this, they carry out ultrasound examination of the gallbladder (ultrasound) and cholecystography, which allow you to identify changes in the gallbladder and the presence of stones. In addition, laboratory tests are carried out: a blood test, urine test, and sometimes cystic bile are taken (taken by duodenal sounding).
Treatment
1. Surgical treatment
stone removal surgery should not scare the sick. Currently, these operations are performed at a good level in almost any hospital, and in some hospitals laparoscopy is performed, that is, a mini-surgery with a pinpoint incision. After the operation, the patient quickly returns to normal life. For anesthesia, drugs of only high quality are used: they do not cause serious trouble to the body, its excretory systems, do not cause severe intoxication, and besides, their action can be suspended at any time. Therefore, if surgery is indicated, if ultrasound and tests confirm the presence of stones, you should not wait for complications. It is better to calmly, during the period when the exacerbation has passed, go to the hospital, prepare for the operation, and after some half a month feel like a healthy, able-bodied person, and not a “stone carrier” at risk.
2. Therapeutic agents
In addition to surgery, there are other methods of treatment - therapeutic. First of all, these are drugs that should relieve an attack, provide emergency therapeutic assistance for biliary colic, save a person from excruciating pain. For this purpose, various antispasmodic drugs are administered.
Choice of a medical specialist various drugs and the method of their administration (intravenously, intramuscularly, subcutaneously) depend on the strength of the attack and the patient's condition. Most often, an attack is relieved by an injection of Platifillin, Papaverine or Dibazol. In the period of an acute attack of biliary colic, intramuscular administration of No-shpa or Eufillin is also effective. Naturally, each of these drugs has contraindications, so doctors choose the necessary drug only after examining the patient.
As a rule, antispasmodics are administered simultaneously with painkillers. Baralgin is especially effective (it relieves spasms and soothes pain). You can use analgesics or make an intravenous injection of Novocain.
If the attack is very severe and it is not possible to remove it with the help of the listed means, then “heavy artillery” is used: special strong drugs are introduced, for example, Tramal in combination with Atropine or other antispasmodics. In some cases, the use of Nitroglycerin is effective. In a hospital setting, a right-sided pararenal blockade is performed.
At severe vomiting Cerucal is introduced (it regulates the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, perfectly relieves nausea and vomiting of a very different nature), you can also use Diphenhydramine, Aminazin or Pipolfen, but the combined administration of these drugs is more appropriate. Drinking solutions of Regidron or Citroglucosolan is also prescribed.
If the attack is not very strong: there are no sharp pains, vomiting (only nausea), then injections can be dispensed with. In this case, the doctor prescribes antispastic drugs: 5-10 drops of a 0.1% solution of Atropine, or Belladonna Extract, Besalol, or Papaverine, No-shpa or Dibazol tablets. Together with one of these drugs for complete pain relief - a Baralgin tablet.
But often, because of nausea, it is difficult to drink the medicine. In this case, the drugs are administered using an enema - an effective and at the same time safe way. For an enema, as a rule, a combination of Eufillin, Belladonna and Analgin is taken.
After the pain stops and nausea subsides, the patient can be given a laxative, but not saline. Salt laxatives have a pronounced choleretic effect, and they should not be taken in the first days after an attack.
Patients have no appetite, and there is no need to force them to eat. Only warm drinks are prescribed: sweet tea, cranberry (sweet) juice, compotes, heated water "Essentuki" No. 4. Complete rest and strict bed rest are necessary.
So, the seizure has been lifted. And, as you can see, there are many opportunities for this. It is only important to use them skillfully in order, on the one hand, to help a person as quickly as possible - to relieve him of pain and relieve all other unpleasant symptoms, on the other hand, not to cause unwanted side effects of medication.
But there is an equally important task ahead - prevent recurrence of seizures, maintain a good state of health, help the gallbladder and biliary tract work and prevent the formation of new stones. For this, other means are used.
Some people, out of naivety and ignorance, do not listen to the opinion of a doctor, but try to help themselves using a cheaper and simpler version of conventional choleretic drugs. They have the hope that the stones will come out on their own. In vain: this will not happen! The stones will not be able to get out, but it’s easy to move from their “familiar” place. As a result, they clog the bile duct - and a person may end up in a hospital bed with an attack of biliary colic.
That is why it is very dangerous to take choleretic drugs in case of gallstone disease without consulting a doctor: allochol, cholenzym, berberine, liobil and others. First you need to undergo an ultrasound examination to determine whether there are stones in the gallbladder or not. If the stones are not found, then the pain syndrome gives cholecystitis and choleretic drugs in this case will not bring harm.
Many people think that when cholelithiasis you can safely drink infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs. But it's not. Immortelle, corn stigmas, aloe, barberry, St. John's wort, oregano, wild rose, calendula, and even valerian - all of these plants also have a choleretic effect and can be a potential danger to people suffering from gallstone disease, as they can cause an attack of hepatic colic.
3. dissolving stones
Medical litholysis(“lithos” - a stone, “lysis” - dissolution) is a method of treating gallstone disease, which began to be developed back in the 70s of the last century. Initially, the dissolution of gallstones was carried out with the help of chenodeoxycholic acid, which, when taken for a long time, inhibits the synthesis of cholesterol in the body and promotes the dissolution of gallstones. But the use of chenodeoxycholic acid in therapeutic doses causes a large number of side effects, therefore, at present, ursodeoxycholic acid, which is also a hepatoprotector, is most often used as a drug for litholysis.
However, when using this acid as a “solvent”, there are a number of restrictions, namely: gallstones must be radiolucent (cholesterol); the gallbladder must function (the cystic duct must be passable); the fullness of the lumen of the gallbladder with stones should not exceed half, etc. In addition, stones with a density of no more than 70-100 units on the Hounsfield scale are subject to dissolution with bile acids.
Given these limitations, only 20% of the total number of patients with cholelithiasis can receive a referral for stone dissolution. But even with the most careful selection of them, the therapeutic effect is not observed in all patients (from 25 to 50%).
General contraindications for dissolving stones by any method:
. acute infectious diseases;
. acute diseases requiring inpatient treatment;
. pregnancy;
. complicated forms of gallstone disease;
. disabled gallbladder, etc.
Cleaning
Cleansing with a mixture of olive oil and citric acid, according to some naturopaths, is quite effective method. Still tubeless tubage if the person has large stones in the gallbladder, it is absolutely impossible to carry out this procedure: a shifted stone will clog the ducts and lead the patient to urgent surgical intervention. Please note that true hard stones larger than 8-10 mm cannot pass
Through the mouth of the bile duct, and those plasticine-like formations that come out during cleansing with oil and lemon are not stones, but clots of old bile.
One of the simplest and most affordable methods of liver cleansing is tubeless tubage. At the preparatory stage, you need to drink antispasmodic tea for 3 days: a drop of rose oil is added to a glass of hot water. Instead of aromatic oil, you can brew a mixture of lavender flowers, rose petals and lemon balm herb (1 teaspoon of the collection per 1 cup of boiling water). Take a glass 3 times a day.
On the day of tubeless tubage, it is better not to eat anything, just drink the above-mentioned antispasmodic tea. If there is no confidence in the effectiveness of such tea, it is necessary to take 1-2 tablets of no-shpy 2-3 hours before the procedure. In the evening, at about 20 o'clock, you should drink a solution of sorbitol: 1 des. Spoon (10 g) of the drug stir in half a glass of hot water. Then immediately lie down with a hot heating pad on the liver area. After 45 minutes, dilute a saline laxative in half a glass of water and drink. Lie down with a heating pad for another half hour.
After that, drink a third of a glass of a mixture of olive oil (you can also use unrefined sunflower oil) with lemon juice in a 3: 1 ratio. Lie down for another 30 minutes.
Then stir in a third of a glass of warm antispasmodic tea and drink. Lie down for another 2 hours on a heating pad. In the presence of pain, it is necessary to take another 1-2 tablets of no-shpy.
Gentle cleansing can be repeated every month. By the way, they also contribute to the destruction of small stones into sand.
mechanical cleaning
Place your palms towards the other to the right side so that the fingers are under the right hypochondrium. Now while exhaling during the cleansing of the gallbladder, pressing with your fingers, deepen your palms as far as possible inward. If the gallbladder is out of order, you will feel pain. If the pain is small, hold your fingers like this for 2-3 minutes. Repeat again, also on the exhale, but try to "climb" even deeper. After that, the pain usually stops.
- C The purpose of the procedure for cleansing the gallbladder is to activate the process of self-purification gallbladder mechanically.
Perform similar exercises with the gallbladder several times a day - on an empty stomach or 3-4 hours after eating. After such pressing, sand and small stones come out, the manifestations of chronic cholecystitis weaken and biliary dyskinesia disappears.
You can not clean the liver and gallbladder in the following cases:
- without preliminary ultrasound - examinations to exclude cholelithiasis;
- there are signs of an infectious disease of a cold or other nature (high temperature, severe headache, weakness, nausea, diarrhea);
- upon the appearance acute diseases internal organs;
— in the period of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- in a state of physical overwork;
- during pregnancy;
—during breastfeeding;
In a state of increased irritability or in a stressful situation.


