Our priority is the development of preschool education
Creation of a system of preschool education in Russia. The concept of "education system" in the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 273 "On Education". Components of the system of preschool education in accordance with regulatory documents.
Determination of the state strategy in the field of system development preschool education(analysis of legal documents governing the development of preschool educational institutions: the National Doctrine of the Russian Federation, the Federal Target Program for the Development of Education until 2020, the Roadmap for the Development of the Preschool Education System in the Russian Federation until 2020, Our New School, etc.). The main directions of development of the system of preschool education in the Russian Federation: the availability and quality of preschool education; development of teaching staff and raising the social status of pedagogical activity; state-public nature of education management; increasing the economic efficiency of preschool education.
Creation of a system of preschool education in Russia. The concept of "education system" in the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 273 "On Education".
It is a multifunctional network of preschool educational institutions (DOE), focused on the needs of society and the family;
Solves the problems of protecting and strengthening the health of children;
Implements a range of educational programs (basic and additional) in accordance with the priority direction of the preschool educational institution and the needs of consumers (variable types of preschool educational institutions account for about 35% of the total number of kindergartens);
Provides a diverse range of educational, health and medical services, taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the child's development;
Creates psychological and pedagogical conditions for the child's stay in preschool;
Interacts with the family on the upbringing, education and development of children preschool age;
It is integrated into the system of continuous education (despite its optionality);
It develops in the conditions of social partnership.
It takes into account regional peculiarities of the development of education.
Advantageous features of the system of preschool education in present stage
The holistic nature of the pedagogical process, its developing and educating nature, the "pre-subject" content of education.
In the conditions of preschool education, the integrity of the medical, psychological and pedagogical support of the child is ensured, which is necessary in connection with the age characteristics of the preschooler, flexibility, mobility and sensitivity in the development of somatics, physiology, and the psyche.
The presence in preschool education institutions of an emotionally comfortable educational environment that develops the child. The variability of the educational space provides children with the opportunity to choose and manifest independence in accordance with their interests and inclinations. The organization of polyfunctional types of children's activities initiates the creation of children's associations in which each child performs a function he likes and at the same time cooperates with other children. In such an educational space, the processes of socialization and individualization leading at preschool age harmoniously complement each other.
National Doctrine of Education in the Russian Federation
The National Doctrine of Education in the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Doctrine) is a fundamental state document that establishes the priority of education in state policy, the strategy and main directions of its development.
The doctrine defines the goals of education and training, ways to achieve them through the state policy in the field of education, the expected results of the development of the education system for the period up to 2025.
The strategic goals of education are closely linked to the problems of the development of Russian society, including:
Creation of the basis for the sustainable socio-economic and spiritual development of Russia, ensuring a high quality of life for the people and national security;
Strengthening the democratic rule of law and the development of civil society;
Staffing of a dynamically developing market economy, integrating into the world economy, with high competitiveness and investment attractiveness;
Assertion of Russia's status in the world community as a great power in the field of education, culture, art, science, high technology and economy.
The doctrine reflects the interests of the citizens of the multinational Russian state and is designed to create conditions in the country for universal education of the population, to ensure real equality of citizens' rights and the opportunity for everyone to improve their educational level throughout their lives.
The doctrine recognizes education as a priority area for accumulating knowledge and developing skills, creating the most favorable conditions for identifying and developing the creative abilities of every citizen of Russia, educating industriousness and high moral principles in him, and also recognizes education as a sphere of employment of the population, profitable long-term investments and the most effective investment capital.
The doctrine reflects the new conditions for the functioning of education, the responsibility of social partners - the state, society, families, employers - in matters of the quality of general and vocational education, and the upbringing of the younger generation.
The doctrine defines the main directions for improving the legislation in the field of education and is the basis for the development of programs for the development of education.
The adoption of normative acts that contradict the doctrine, including those that reduce the level of guarantees of the rights of citizens in the field of education and the level of its financing, is not allowed.
The doctrine reflects the determination and will of the state to assume, together with the public, responsibility for the present and future of national education, which is the basis of the socio-economic and spiritual development of Russia.
Expected results of the implementation of the doctrine
The quality of education
The state policy in the field of education provides:
Creation of a democratic education system that guarantees the necessary conditions for full-fledged quality education at all levels;
Individualization of the educational process due to the variety of types and forms of educational institutions and educational programs that take into account the interests and abilities of the individual;
A competitive level of education both in terms of the content of educational programs and the quality of educational services.
Availability of education
To all citizens Russian Federation regardless of gender, race, nationality, language, origin, place of residence, attitude to religion, beliefs, membership in public associations, age, state of health, social, property and official status, the following is ensured:
Public and free pre-school education;
Compulsory and free basic general education;
Public and free secondary (complete) general education, including the possibility of choosing the main profiles of education;
Public and free primary vocational education;
Free higher and secondary vocational education on a competitive basis;
Free postgraduate education on a competitive basis in graduate school, doctoral studies;
Additional education for children - on the basis of targeted financial support for children from low-income families;
Public and free special education for persons with disabilities health opportunities.
Remuneration of teaching staff
The wages of educators will grow at a faster pace than the average in industry, due to an increase in the share of expenditures on education in the state budget, expanding the independence of industry organizations and stimulating the effective use of budgetary and extrabudgetary funds.
This will make it possible to achieve a level of wages that ensures the sustainable competitiveness of education in the labor market and gradually bring wages closer:
Teachers and other teaching staff to the average salary of industrial workers in the Russian Federation;
Other employees of educational institutions to the average wages of similar categories of industrial workers in the Russian Federation.
Already at the first stage, the remuneration of teachers from among the teaching staff of educational institutions of higher professional education will be close to twice the average wage of industrial workers in the Russian Federation.
Pension provision
On the basis of wage increases and the creation of a sectoral pension system, educators will be provided with a decent level of pension provision.
Already at the first stage, the creation of an industry-specific professional pension system for educators will begin. Due to this system and the funds of educational organizations, in particular, increased old-age pensions for faculty, researchers and other categories of pedagogical workers will be provided.
At the same time, pedagogical workers with a teaching experience of more than 25 years, in return for a pension for years of service, will be given the right to receive an allowance for work experience if they continue their teaching activities.
Social security of students, pupils, students and graduate students
Children and youth studying in educational institutions are guaranteed:
Protection of life, preservation of health, physical education of preschoolers, students, students and graduate students;
Targeted provision of academic and social scholarships, as well as statutory benefits to students and students from low-income families and other specific categories of students;
Assistance in employment and employment of students, graduate students, graduates of educational institutions.
Financing the education system
The state policy in the field of financing education is obliged to ensure at the first stage the outstripping growth of expenditures on the education system in the total volume of public expenditures and a significant increase in their efficiency, the creation of conditions for attracting funds from extrabudgetary sources to the education sector.
To achieve the goals and objectives defined by the doctrine, the achievement of the next level of financing of the education system is ensured.
At the first stage (until 2004), the growth rates of budgetary funds will outstrip the growth rates of the total volume of budget expenditures.
Starting from 2001, targeted funds will be provided for the development of education, including the informatization of educational institutions.
Opportunities to attract funds from family budgets and other non-budgetary sources to the education sector will be expanded.
At the second stage (until 2010) - it is necessary to ensure the growth rates of budget financing of education in accordance with the GDP growth rates. Additional funding will come from family budgets and enterprise funds.
At the third stage (until 2025), while maintaining the growth rate of budget financing, there will be a further increase in the flow of financial resources into the education system from various extra-budgetary sources.
In the relevant budgets for the next financial year, as well as from other sources established by law, funds should be provided in the amounts necessary to implement the provisions of the current legislation on education in the Russian Federation.
Education determines the position of the state in the modern world and of a person in society. Domestic education has deep historical traditions, recognized achievements: in the 20th century, Russia became a country of universal literacy, was the first to go into space, reached the forefront in all areas of fundamental science, and significantly enriched world culture.
In the last decade, many of the achievements of Russian education have been lost, so the doctrine is designed to help change the direction of state policy in the field of education, to strengthen in the public mind the idea of education and science as the determining factors in the development of modern Russian society.
The priority development of education on the basis of this doctrine is designed to lead Russia out of the crisis, to ensure the future of the nation, a decent life for every family, every citizen of Russia.
Determination of the state strategy in the field of development of the system of preschool education
Khutornaya Tatiana
Priority areas of work of preschool educational institutions in the context of the introduction of the GEF of preschool education
PRIORITY AREAS OF WORK
MBDOU Kerch RK "Kindergarten of combined type No. 2 "Droplet"
AT CONDITIONS FOR THE INTRODUCTION OF GEF BEFORE
Maintaining the Federal State educational standard preschool education is associated with a number of transformations:
The emergence of new conditions(Society's request, change in state policy, update of quality requirements education);
The emergence of new legal documents that regulate the activities preschool organization(Law on education, GEF) ;
Engage parents in active partnerships.
« Preschool education- developing and developing- these words perfectly reflect the life of today's kindergartens in Crimea. New law on education, new charter, new instructions, new educational programs aim us at new tasks, and therefore at new areas of work which provide holistic assistance to the personal development of the child. In the current terms of education not only changes, but also gives impetus to innovative processes. The teachers of our kindergarten are looking for aimed at turning the educational process into a living, interested communication of the child with adults and peers in different types activities.
The priority areas of work of our preschool institution are: physical, moral, artistic and aesthetic development preschoolers.
Implementation of new quality requirements preschool education involves close attention to physical education, the effectiveness of which is achieved through the use of the entire system of means - these are the healing forces of nature, hygiene factors, physical exercises. We use a lot of games and outdoor activities. Work physical treatment room helps to reduce morbidity.
AT work used with children various forms of physical culture classes: plot, game, thematic, complex, educational and training nature, developing classes "Physical Education Theatre"(stretching gymnastics, separate physical education classes for girls and boys). Through networking, our preschool the institution cooperates with the TV and radio company "Kerch". Children became participants in the TV show "Island", which presents morning exercises in verse "Africa Journey" and entertainment "Winter morning". These programs promote healthy image life and creating the spirit of a single team with parents. The result of our work- these are prizes in competitions among teams of preschool educational institutions "Fun Starts" which have become a tradition and are held annually in our city on April 11, the Day of the Liberation of Kerch from Nazi invaders.
Patriotic education is an integral part of our work with children. A system has developed in the preschool educational institution work to familiarize children with their native city, its glorious, heroic history, to form citizenship and patriotism.
The upbringing of a humane, spiritual and moral personality contributes preschool work institutions for multicultural education. Over the years, the teaching staff works on the problem of the formation of social competence preschooler in conditions multicultural space. We see the need to continue the experimental work. Taking into account the national and cultural characteristics of the region, the tasks are defined work:
Raising love for the Crimea, awareness of its multinationality;
Formation of a common culture, taking into account the ethno-cultural education;
The development of tolerant relationships.
The formation of multicultural competence is promoted by social partnership with the society of Tavrika, with preschool educational institutions « gold fish» Urban settlement Shchelkino. Creative group in the framework of experimental activities works on the creation of a calendar of holidays of the peoples of the Crimea with methodological recommendations for their implementation.
Artistic and aesthetic line of work covers several directions: musical activity, artistic speech and pictorial. In the course of implementing the tasks of artistic and aesthetic education, we pay special attention to supporting talented children. Implementation of this directions provided on the basis of the federal target program "Children of Russia", which provides for the "Creation of a system for the identification, development and targeted support of gifted children." Work backed up by command education on the preparation and holding of the annual competition "Funny notes". DOW created terms for training and development of creative abilities preschoolers. The results of this directions is to create a system of support for gifted children through a network of competitions, competitions and other events at various levels. The guys take part in city competitions, remotely - regional ones. In the competition "Constellation preschool children» Kamneva Olya was noted as a young artist (teacher Degtyaruk Alexey Alekseevich, as a vocalist Tkachuk Evelina (teacher Tkachuk Elena Petrovna). A drawing competition was held in this educational goal "Our friend traffic light", "Golden Autumn" and competition of handicrafts from natural material "Gifts of Autumn" with the participation of parents. The autumn entertainment festival surprised educators and parents with the radiance of new little talents, who now need to be given the opportunity to realize their own "I" support and help. Created in kindergarten terms for creative work in the art studio, music and sports activities in the music and sports halls. Provided social partnership with municipal organizations "School of the Arts", "sports and music schools".
For successful entry into GEF DO and the implementation of priority tasks in the DO, a roadmap has been developed, where
Psychological and pedagogical
methodical
Personnel support
The leading role in this is assigned to the personnel issue.
Usage various forms of work with teachers(seminars, workshops, business games, a bank of ideas, a master class, a union of like-minded people, a circle of quality) determines the successful entry into the Federal State educational standard.
AT conditions dynamic processes for the implementation of selected directions the competence and pedagogical mobility of teachers is important, which provides
Continuous improvement of pedagogical culture;
Skills self-educational work;
Possession of techniques information processing;
ICT competence.
The combined efforts of the teaching staff allow us to solve the tasks set, to ensure the interaction of subjects educational process, openness preschool educational organization , involve parents in the management of the pedagogical process in order to see the possibilities of holistic assistance to the personal development of each individual child.
LECTURE V. The system of preschool education
The ideas of humanization and democratization are put in the basis of the state policy in the field of education. They are reflected in the Constitution of the Russian Federation (1993), the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" (1992). The documents note that education is understood as a purposeful process of training and education in the interests of the individual of the society, the state. The right to education is one of the fundamental and inalienable constitutional rights of citizens of the Russian Federation.
The education system in the Russian Federation is a combination of a system of successive educational programs and state educational standards of various levels and directions; networks of educational institutions of various organizational and legal forms, types and types that implement them; the system of educational authorities and institutions and enterprises subordinate to them (see the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education”, Section 2. Article 8).
Preschool education is the first link in the Russian education system. This idea was written down as early as 1918 in the “Regulations on a unified labor school”. From an early age, the child is guaranteed the right to education, which, from the standpoint of the Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989), includes the following aspects:
Opportunity to visit an educational institution;
Creation of conditions for educational activities;
Relations between participants in the educational process based on respect for the human dignity of the child (see Doronova T.N. The right to education / / preschool education - 2001. No. 10, p. 2-6)
The system of preschool education is constantly changing, improving and updating. It fulfilled and fulfills the most important social order of society, is one of the factors of its development. The Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" (Article 18) supports the role of parents, who are the first teachers. Their duty is to develop the foundations of the physical, moral and intellectual development of the personality of the child in infancy. A network of preschool educational institutions operates to help the family. Today, there is no single view of preschool education in society. There is an opinion that kindergartens are not needed, that the education of preschool children can be left at the mercy of parents, and that it is they who have the right to independently decide how and where to prepare a child for a future stage of education. Perhaps, for a certain, small part of the Russian population, the idea of education vouchers is acceptable. But analytical data show that the vast majority of parents with children of preschool age need the services of preschool educational institutions. Therefore, the Ministry of Education considers the preservation and development of the network of preschool educational institutions the main strategic task of the Department of Preschool Education.
Russian preschool educational institutions in their activities are guided by the Model Regulation on a preschool educational institution (1995), which regulates the activities of state, municipal educational institutions. It defines the tasks of a preschool educational institution: protecting the life and health of children; ensuring the intellectual, personal and physical development of the child; introducing children to universal values; interaction with the family to ensure the full development of the child.
Modern preschool institutions are characterized by multifunctionality, diversity, freedom in choosing the priority direction of the educational process, polyprogramming in the implementation of content. All this lowers the level of variability, independent activity of preschool educational institutions, and adaptability to regional conditions. In accordance with the Model Regulations, the system of preschool educational institutions includes the following types:
Kindergarten with the priority implementation of one or more areas of development of children (intellectual, artistic and aesthetic, physical, etc.).
Kindergarten of a compensating type with priority implementation of qualification correction of deviations in physical and mental development pupils;
Kindergarten of supervision and improvement with priority implementation of sanitary-hygienic and health-improving measures and procedures;
Kindergarten of a combined type (which may include general developmental, compensatory and recreational groups in various combinations;
Child Development Center — Kindergarten with physical and mental development, correction and improvement of all children.
Thus, a preschool educational institution type of education systems include various types that have their own distinctive features (usually associated with the model of the educational process, the basis of which is the educational program).
However, all types of preschool educational institutions, realizing the tasks of raising and educating children, are based on the principles of secular education.
A special section of the Model Provision explains the procedure for creating, registering a PEI, and issuing a license (permit) to them. In accordance with the law of the Russian Federation "On Education" (Article 13) and on the basis of the Model Regulations on Preschool Educational Institutions, each preschool institution creates its own Charter. The charter is a document that defines the work of the institution, goals and objectives, the main areas of work, the variability of the educational programs used. The Charter defines the rights and obligations of participants in the educational process, the main characteristics of the organization of the educational process, additional paid educational services.
Children from 2 months to 7 years old are admitted to a preschool educational institution on the basis of a medical report, that is, the Model Regulation proposes the procedure for recruiting preschool educational institutions, the quantitative composition of groups, their occupancy depending on age.
In the section "Participants in the educational process" it is indicated that they are pupils, parents (or persons replacing them), pedagogical workers. The parental agreement regulates the relationship between the preschool educational institution and parents. The pedagogical value of this section of the Model Provision lies in the fact that the stylistic relationship between the child and the teacher is clearly defined here.
These relationships are built on the basis of cooperation, respect for the personality of the child and giving him the freedom to develop in accordance with individual characteristics.
Persons who have the necessary professional and pedagogical qualifications, confirmed by documents on education, are accepted for pedagogical work. On the basis of Article 53 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education", persons to whom it is prohibited by a court verdict or for medical reasons, as well as persons who have a criminal record for certain crimes, are not allowed to teach.
Article 55 of the Law of the Russian Federation defines the rights, social guarantees and benefits of employees of educational institutions. The charter of the kindergarten, the employment contract (contract) specify these provisions (for example, a ped. worker, at least every 10 years of continuous pedagogical work, has the right to a long vacation for up to one year).
All employees of the preschool educational institution are certified. Young professionals (graduates educational institutions) are certified after three years of operation. In the section “Management of a preschool educational institution” of the Model Regulations, it is written that the general management is carried out by the Council of Teachers, and the procedure for its election and competence is determined by the Charter of the preschool educational institution. The direct management of the activities of the preschool educational institution is carried out by the head. Thus, the system of preschool education is based on the principles of state policy in the field of education, has a legal framework. This system fulfills the needs of society in education and development of children from an early age. A preschool educational institution, performing various functions of its activities, is responsible for the quality of its work, for the compliance of the results of activities with the state educational standard.
Standard(in translation With English - sample, basis, measure) includes federal and national-regional components (Article 7 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education". The educational standard determines the mandatory minimum content of basic educational programs, the maximum amount of teaching load for students, requirements for the level of graduates. Development of an educational standard for preschool educational institutions began in the early 90s (R.B. Sterkina). Today, the temporary state educational standard for preschool education is designed as a system of state requirements for the psychological and pedagogical conditions for raising and educating children. In the Draft State Standard, the content of preschool education is differentiated by the following directions: physical, cognitive-speech, special-personal, artistic-aesthetic.This content is implemented in one or another educational program. Among the requirements to the content and methods of education and training implemented in the preschool educational institution, two groups are distinguished - meaningful and personal,(See R. B. Sterkina. Once again about state educational standards / / Preschool education, 2002, No. 5). The requirements of the first group (substantive) are correlated with certain subject areas and orient the specialist to the selection of a certain content of preschool education (for example, in the field of natural sciences, ecology, health - adults create opportunities for familiarizing children with the physical properties of objects and phenomena with the diversity of flora and fauna, variety of life conditions on Earth). The requirements of the second group (personal) set guidelines for the nature of the interaction of teachers with the child and are aimed at developing his social and personal qualities (curiosity, initiative, independence, interest, etc.).
These requirements make it possible to establish a psychological and pedagogical sequence in the implementation of content, forms, and methods.
Federal component of the standard acts as an invariant part, not subject to change on the ground, ensures the preservation of the best traditions, the further development of the system of preschool education. The federal component of the state. The standard creates the unity of the educational space on the territory of the Russian Federation, regulates the quality of this education, is the basis for the certification of preschool educational institutions, an objective assessment of the level of education.
National regional component of the state educationalstandard reflects socio-economic; national-ethnic, natural-climatic, cultural-historical features of the region (region). This component supplements the mandatory minimum of the content of the educational program, implements in the preschool educational institution. The supplement should be organic and fit naturally into the main educational program of the institution. An example of the implementation of the national-regional component can be the regional educational program for preschoolers "Our Home is the Southern Urals", built on the ideas of folk pedagogy, which are humanistic in content and universal in use. (See Babunova E.S. Regional educational program for
preschoolers "Our home is the South Urals" and the problems of establishing the regional component of the standard of preschool education in the Urals Federal District // Bulletin of the Institute for the Development of Education and Upbringing of the Younger Generation at the GPU. Center for student-centered and developmental education. Series 3. The problem of the development of the personality of a preschooler in the educational process).
At present, in accordance with the letter of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated September 23, 2002, No. 03-51-142 in / 23003 p. The following programs operate on the territory of the Russian Federation: “Rainbow”, “Development”, “ Childhood”, “School 2100”, “Gifted Child”, “Origins”, “From Childhood to Adolescence”, “Golden Key”, “Community”, “Baby”, etc. The quality of programs and pedagogical technologies is ensured by the Federal Expert Council ( see Krulekht M. Innovative programs of preschool education / / Preschool education - 2003, No. 5, pp. 74-79).
The Concept for the Modernization of Russian Education for the Period up to 2010 puts forward the task of ensuring the quality of education, including preschool education.
With updating the content of preschool education associated with an increase in its quality. Updating the content requires both a positive experience in organizing the educational process of a preschool educational institution, and a critical rejection of the negative trends that have developed in the preschool educational system. (See Amend A.F., Zhukova M.V., Frolova E.V. Preschool educational system: problems and Ways to solve // Bulletin of the Institute for the Development of Education and Upbringing of the Younger Generation at ChSPU, Series 3. The problem of the development of the personality of a preschooler in the educational process, Chelyabinsk, 2003.
The main approaches to updating and selecting the content of the preschool level of education are disclosed in the article by L.A. Paramonova (see Paramonova L.A. The content of the preschool level of education: what is the reason for its renewal / / Preschool education - 2003, No. 3). According to the author, the modern basic content preschool education should be selected and line up according to the following principles:
The developmental nature of education, aimed at revealing the potential of the child;
The systemic nature of education (ensuring the interconnection of objects and phenomena that are known by the child and appear in the system);
The integrative nature of education (the development of children based on sensory and rational cognition their level corresponding to their age;
The multicultural nature of education (introducing children to their own culture and traditions, as well as the culture of other peoples, fostering a sense of tolerance, tolerance for the opinions of others, the ability to civilly express their disagreement, discontent, resentment);
The activity nature of education (providing various types of activity, the activity itself in development, its main components: purpose, choice of means, finding ways, control, etc.);
Health-saving character (formation of a healthy lifestyle, hygiene habits, the need for systematic sports, ensuring a health-saving environment).
In the articles by T.M. Babunova, V.I. Turchenko, the main directions of development of the system of preschool education at the present stage are the transition to personality-oriented interaction, a personalized approach, respect for the personality of the child, his rights, creating conditions for the development of the child's subjective position in various forms activities (see Babunova T.M. Modernization of the content of the educational process of a preschool institution. See Turchenko V.I. Updating the content of preschool education in the context of the implementation of the State Standard project // Actual problems of preschool education: Collection scientific papers. - Magitogorsk: MaSU, 2003).
The implementation of integration ideas as a way to update the content and method of preschool education is reflected in the article by G.M. Kiseleva, Yu.N. Ryumina. S.M. Zyryanova (see Kiseleva G.M., Ryumina Yu.N., Zyryanova S.M. Implementation of the ideas of integration in the theory and practice of preschool education / / Actual problems of preschool education: All-Russian interuniversity science, conferences. -Chelyabinsk : Publishing house - in ChSPU, 2003, pp. 208-217).
An integrative approach involves the formation of ideas about a holistic picture of the world; it is based on natural-scientific, aesthetic, social, and logical-mathematical relationships. Integration makes the process of assimilation of the content of education small in volume, but capacious, deep (L.M. Klarina). The principle of integration is well implemented in the educational program "Childhood", St. Petersburg, 1995.
Thus, the content of preschool education is a backbone element that reflects social, economic, and pedagogical changes in the life of society.
More details about the specifics of the implementation of the social and personal development of children, as a basic component of the content of education, can be found in the teaching aid T.M. Babunova, E.S. Babunova, L.V. preschool education process: Educational and methodological manual for daytime students and correspondence departments - Magnitogorsk: MaGU, 2002).
The domestic system of preschool education is unique in many ways: at the request of parents, a child can stay in kindergarten all day (12-hour stay) or around the clock. The educational process is carried out by teachers, medical workers, while parents pay only 20% of the total cost of maintaining children. The maintenance of expenses for the maintenance of preschool educational institutions between the budget and parents is considered mainly as a management problem (E.S. Komarova). However, this socio-economic situation can also be considered as a socio-pedagogical one. (See Organizational and methodological foundations for the development of new forms of preschool education / / Preschool education, 2002 - No. 11, pp. 2-4).
Taking into account the draft Decree of the President of the Russian Federation "On guarantees of the right of citizens to receive preschool education" and the draft decree of the Government of the Russian Federation "On measures to preserve and develop the system of preschool education", "On the creation of the Council for Preschool Education, 2002), an all-Russian experiment was launched to organize new forms of preschool education on the basis of a short stay of pupils in kindergarten. The results of this experiment are summarized in the book "Invites Kindergarten", M., 2002.
Here are short stay patterns children (organization of a weekend group; adaptation groups; groups focused on preparing for school). A description of the new forms of the system of preschool education is given in the article by O.M. Mukhametshina (see Mukhametshina O.M. Some aspects of the regulatory, legal and organizational and methodological support for the work of the Magnitogorsk Education Department on the development of new forms of preschool education / / Bulletin of the Institute for the Development of Education and Upbringing of the younger generation at ChSPU Series 3. (p. 40-43) In the city of Magnitogorsk, kindergartens for children with various health disorders, social support for children from low-income families, for musically gifted children, early intellectual development, young hockey players.
The variety of ways to update the content of the preschool education system raises the question of improving the training of teaching staff, the implementation of the creative activity of preschool teachers, the formation of personal qualities from the point of view of ideas humanistic psychology and pedagogy. The pedagogical potential of the educator, his orientation to the personality of each child, the increase of professional competence, the adoption of the position of active self-education and self-education, the development of pedagogical reflexivity and thinking are resources for the development and modernization of the preschool education system.
Questions for self-examination:.
1. What does the concept of "education system" include?
2. Why is preschool education the primary link in the Russian education system?
3. What are the strategic lines for the development of preschool education at the present stage? What are they caused by?
4. Expand the structure of the Model Regulation on a preschool educational institution?
5. What is the significance of the State Educational Standard in the activities of preschool institutions?
6. What are the ways to update the system of preschool education? What are they due to?
7. What social and pedagogical opportunities do you see in the new organizational and methodological forms of the preschool education system?
Program for the development of a preschool educational institution
Modern trends in the development of preschool education
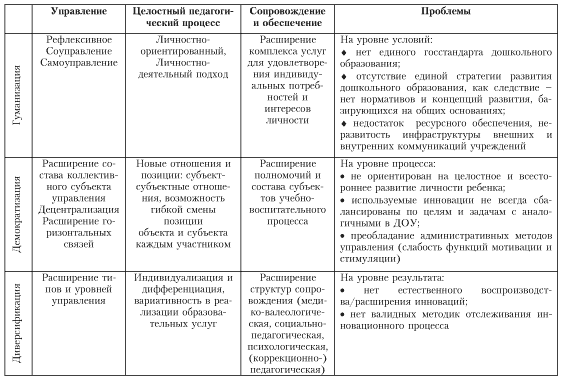
The ongoing transformations in the system of preschool education are due to the objective need for an adequate change in social development and the development of the educational system, which is reflected in the awareness of the pedagogical community of the need for significant changes in the previous course of the functioning of the institution. The main mechanism for optimizing the development of the preschool education system is the search for and development of innovations that contribute to qualitative changes in the activities of a preschool educational institution (DOE), which is expressed in the transition of institutions to the development mode.
Today, we can confidently state the fact of the formal or meaningful transition of most preschool educational institutions to the search mode. This mode is transitional on the way to qualitative changes and the transfer of preschool educational institutions to the development mode. Another aspect is related to the qualitative features of this transition: to what extent the innovations implemented in the preschool educational institution correspond to the urgent needs and opportunities for its development, satisfy the interests and needs of children, parents, teachers, and contribute to the achievement of sustainable high development indicators. Therefore, the issue of determining actual problems in the development of preschool educational institutions becomes the most important.
The analysis of existing concepts, projects and programs in the field of preschool education allows us to identify a number of basic trends in the development of the system:
humanization- determines the primacy of the personal development of subjects (parents, teachers, children), the centering of the educational process on the values of human development, the orientation towards the comprehensive and harmonious development of the personality, the transfer of the subject to the position of self-managed development in the process of revealing the essential forces. The humanization of education is a process aimed at developing the personality as a subject of creative activity, which "is also the most important characteristic of the lifestyle of teachers and pupils, which involves the establishment of truly human (humane) relations between them in the pedagogical process" and is a key component of the new pedagogical thinking, focused around the idea of personality development. The leading direction of the humanization of education counts "self-determination of personality in culture", its familiarization with national and cultural traditions enriched with the human content of humanization - increased attention to the personality of each child as the highest social value of society, setting on the formation of a citizen with high intellectual, moral and physical qualities;
democratization is associated with the expansion of the rights and powers of the participants in the educational process, the focus on meeting the individual needs and requests of the subjects. This involves the creation of prerequisites for the development of activity, initiative and creativity of pupils and teachers, their interested interaction, as well as broad public participation in the management of preschool education;
diversification is defined as a necessary and sufficient variety of types and types of institutions, educational services and approaches to their implementation in order to meet the diverse and versatile needs of participants in the educational process in a preschool educational institution.
The projection of the identified foundations on the educational process in a preschool educational institution presents all its subsystems in a new way.
In this regard, a number of basic principles appear that ensure the implementation of these areas in the development process of the preschool educational institution and its participants:
The principle of human conformity (the unity of cultural and natural conformity);
- the principle of the integrity of the pedagogical process and the complexity of goals;
- the principle of activity and equal partnership in the pedagogical interaction of all subjects of the pedagogical process.
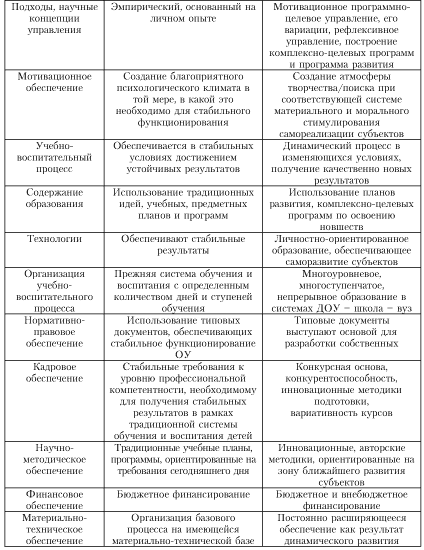
The modernization of the management of a preschool educational institution is associated with a variety of types and management technologies that provide a comprehensive and comprehensive impact of the management system on the managed system of preschool educational institutions within the framework of motivational and program-targeted approaches, motivational program-targeted management, co-management, reflexive management and self-government. Indicators of the qualitative transformation of the management of preschool educational institutions are primarily new principles:
Democratization and humanization;
- consistency and integrity of management;
- centralization/decentralization;
- interconnections and separation of strategic, tactical and operational levels of management and their respective types of management (traditional, reflexive, self-management);
- unity of command and collegiality;
- objectivity and completeness of information in making managerial decisions.
At the present stage, there are a number of problems in the development of the innovation process in preschool educational institutions, in particular, such as:
combining innovative programs with existing ones in preschool educational institutions;
the split of the pedagogical community and the coexistence of representatives of various pedagogical concepts;
non-compliance of new types of preschool educational institutions with the expectations and requirements of parents;
the need for new scientific and methodological support for ongoing educational activities;
the need for new teaching staff;
adaptation of innovations to new conditions;
the problem of changing, optimizing, replacing innovations, the ability to get rid of outdated, pedagogically inappropriate in time;
the problem of reproduction of innovation and formation of conditions contributing to this.
Based on the analysis of existing concepts for the development of preschool education, the leading areas of innovation in preschool education include the assertion of humane subject-subject relations, the development of creative abilities, the intellectual powers of children; individual creative development of the child's personality; development of communication between practitioners and researchers in the field of innovation.
The change in the paradigm settings of modern education makes it possible to consider the development of a child as a process of his self-development, where education is a form of mental development of a preschooler, and development standards are transformed into an understanding of development as a norm (V.T. Kudryavtsev, 1999).
Accordingly, the main trends in the development of preschool education are associated with the installation of a full-fledged space for the development of the child and the organization of comprehensive support for the individual development of preschool children. A rich and safe life, eventfulness, connectedness of an adult and a child in the educational process, the priority of developing and educational tasks in preschool educational institutions contribute to the favorable socialization of children and lay the basic competencies of a preschooler in mastering the world and appropriating culture.
Part I. Preschool educational institution as an open developmental system
1.1. Structural and functional model of the activity of a preschool educational institution as an open and developing system
A preschool educational institution as a system is a complex socio-psycho-pedagogical education, consisting of a combination of: a) system-forming factors, b) structural and c) functional components, d) operating conditions.
a) system-forming factors are represented by the mission, concept and development program, partial programs that fix the set of leading ideas, the goal and result of the activities of the preschool educational institution;
b) the structural components are indicated by the control and managed systems, their composition (educators, parents, children), as well as the technologies of the activities of subjects at all levels of management regarding the implementation of program content in the preschool educational institution;
c) the functional components are determined by the appointment of managerial functions in the activities of the preschool educational institution (analytical-diagnostic, motivational-stimulating, planning and prognostic, organizational and executive, control and evaluation, regulatory and correctional) for the formation of interconnected activities in the system "teacher - child - parents" and relevant subsystems;
d) the conditions for the functioning of the preschool educational institution are determined by the existing spaces of its activity - medical-valeological, social, psychological and pedagogical environments, time frames and psychophysiological characteristics and capabilities of the participants in the educational process in the preschool educational institution.
Modern tendencies in the development of preschool education
The openness of a preschool educational institution as a system is determined on the basis of the development spaces that exist in the institution, as well as the dynamics of their changes.
The characteristics of the openness of a preschool educational institution can be the degree of non-equilibrium of its state (relatively stable, but not absolutely changeable), the mechanism of self-regulation and the nature of the reaction to environmental changes (adaptation or super-adaptive activity), the type and degree of regulation of the control system (traditional or innovative, the predominance of vertical or horizontal connections), etc.
The main result of the functioning of an open system will be successful interaction with the society, mastering which the preschool educational institution itself becomes a powerful means of socialization of the individual. The comprehensive and harmonious development of the child's personality can be ensured by a complex impact on all aspects of his activity. The complex impact is based on a set of interconnected spaces for the development of subjects of education within a preschool institution.
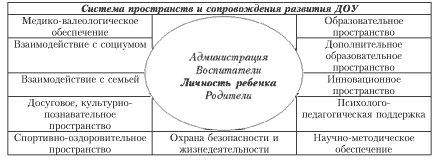
The allocated spaces are necessary and currently sufficient for the majority of preschool educational institutions in order to ensure the required level of reproduction of the results of the innovative activities of the institution.
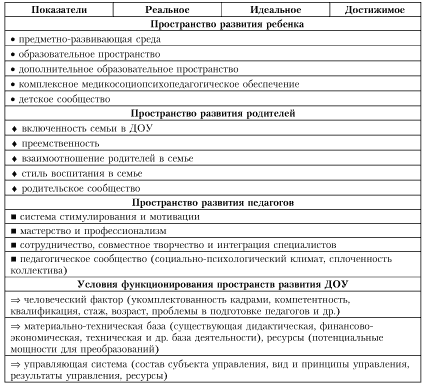
Modeling and designing the development process of a preschool educational institutionFor the full development of an educational institution, it is necessary to build a project of its activities for the foreseeable future, taking into account the model of a preschool educational institution and the mechanism for the gradual transformation of its components.
At the same time, the model in our understanding will be the system of spaces of the preschool educational institution, fixing the development of the subjects of the educational process in interaction, as well as indicators of their interconnected activities.
The model presented in the diagram space for the development of a preschool educational institution performs criteria-diagnostic, planned-prognostic and developing-forming functions that allow optimal management of the institution's activities.
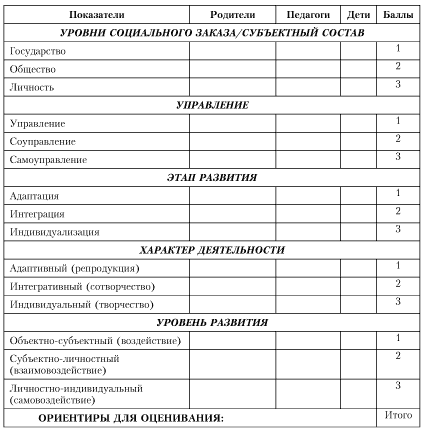
The space for the development of a preschool educational institution (DOE) consists of three interconnected spaces for the development of its subjects: educators, parents, and children. The main structural unit in the process of development of the preschool educational institution is the interaction of participants in the educational process in the system "teacher - child - parent". By describing the specifics of the functioning of this system, we come to understand the direction and purpose of the allocated spaces for the development of all subjects: parents form a social order at the level of social need, educators are direct implementers of educational services at the state level, children act as consumers of educational services provided by preschool educational institutions for training, education , personal development.
Space for the development of a preschool educational institution
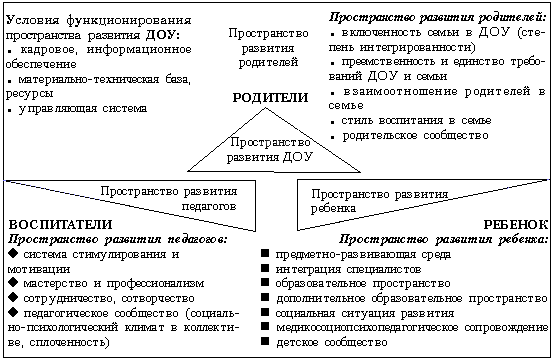
The logic of the deployment of development processes in each of the spaces is to change the stages and levels of development: adaptation, integration, individualization. The identified stages, on the one hand, fix the continuity and quantitative transformation of changes, on the other hand, determine the levels that characterize the qualitative changes in a particular space of development of a preschool institution.
At the stage of adaptation, the actualization of the potential for development and self-development of teachers, parents, children is ensured, conditions are created for their transfer from the position of an object to the position of a subject of their own life activity.
The stage of integration is associated with the provision of development and self-development by means of interaction in the system "teacher - child - parent" in the form of co-creative productive activity and communication. The result of this stage is the transfer of teachers, parents, children from the position of the subject into the personal context of life fulfillment.
The stage of individualization is connected with the analysis of the degree of isolation of the personality of the teacher, parent, child in the corresponding integrated community and the determination of the development potential in the process of maximum disclosure of the individual essence of the subjects.
The logic of the deployment of socio-psychological and pedagogical support for the individual development of subjects in a preschool educational institution

Integration of the above spaces makes it possible to develop a mechanism for complex medical, social, psychological and pedagogical support of the individual path of development of each subject in logic:
a) the structural organization of the social order in the field of preschool education. If we single out the aspects of social ordering formed at different levels community development and development of the educational system, we will get federal, national-regional and intra-institutional (DOE) components, simultaneously representing the structural elements of the State Standard in the field of preschool education;
b) change of stages and levels of deployment of the subject's essential forces. The representation of social development as a change in certain stages of the subject's socialization allows us to fix the logic and direction of the development of all subjects of the educational process in the preschool educational institution (adaptation, integration, individualization);
c) changing the leading types of management in the preschool educational institution. The selected types of management develop along the line “from simple to complex” - from the predominance of predominantly external influences to internal ones, from focusing on a collective prescription to the primacy of self-programming and managing one’s own development (traditional management, motivational program-targeted management, co-management, reflexive management, self-management) ;
d) changing the leading forms of interrelated activities of the subjects of the development process of the preschool educational institution. Fixed in such concepts as "impact", "interaction", "self-influence", the trajectory of the development of children, parents, teachers in joint activities appears to be the main mechanism for changing the forms and types of management proposed above.
1.2. Modes of life of a preschool educational institution
There are two main modes of operation of a preschool educational institution. Below are the main characteristics of each type and their distinctive features.
The activity of the preschool educational institution in the development mode is a purposeful, natural, continuous and irreversible process of the transition of the institution to a qualitatively new state, characterized by a multi-level organization, cultural and creative orientation and the use of an ever-expanding development potential.
The activity of the preschool educational institution in the mode of operation is the life process of the preschool educational institution, aimed at the stable maintenance of a certain state, characterized by cyclical repetition, reproduction of accumulated experience and the use of accumulated potential.
The table below allows you to determine the nature of the life of a particular institution based on the main indicators of the modes of development and functioning.
The main characteristics of the life modes of preschool educational institutions
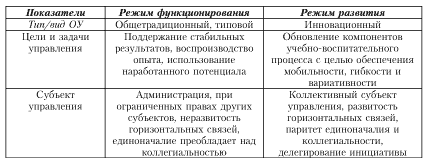
Signs of the activity of the preschool educational institution in the development mode:
the relevance (significance and timeliness) of the ongoing work aimed at developing practical measures to solve a serious problem;
the involvement in the search activities of the majority of teachers, the innovative potential and climate of the team, as well as the balance of interests of all participants in innovative activities;
characteristics of the results: efficiency, productivity, optimality;
indicators of innovative development: sustainability, reproducibility;
qualitative transformation of the management system, all components of a holistic pedagogical process and the conditions for its implementation in a preschool educational institution.
Conditions for the development of preschool educational institutions and sources of development ideas:
a clear statement of the goal based on a comprehensive problem analysis;
the presence of a development concept;
availability of staffing, material and technical base, scientific and methodological support, resources for the forthcoming work;
a favorable socio-psychological climate in the team, the readiness of teachers to implement the development program, the satisfaction of the subjects with the current results of work, the balance of interests of all participants in the innovation process;
providing freedom of choice in solving tasks;
selection of pedagogically expedient, optimal technologies for innovative activity;
use of the educational potential of the society;
expansion of external relations, openness of the preschool educational institution;
organization of expedient management, optimal combination of types of management;
studying and using the positive experience of other preschool educational institutions, creating an innovation bank.
The logic of transferring the preschool educational institution to the development mode is associated with the implementation of the main functions of management, analysis, planning, organization, control and regulation of the transformation process.
A detailed analysis of the activities of a preschool educational institution according to the selected indicators allows us to present a set of interrelated criteria for assessing the current and potential level of its development. They are based on the understanding that the identified stages and levels of development of the institution as a whole and its individual spaces are determined by a single logic of the development of subjects.
A system of interrelated criteria for assessing the current and potential level of development of a preschool educational institution

Attention should be paid to the possibility of fixing the actual and potential development of the institution based on the proposed criteria. The logic for determining the identified levels of development fits into the scheme for describing the actual and ideal state of the preschool educational institution, as well as the system of steps to transfer the institution to the desired state by determining the achievable level of development of the preschool educational institution on the existing base, with the involvement of external modernization resources.
The use of such an algorithm makes it possible to identify problem areas in the functioning and development of a preschool educational institution, plan a system of actions and organize work to overcome the identified contradictions, determine the intermediate and final results of such activities, correct shortcomings in a timely manner, and also predict further lines of development of preschool educational institutions.
This format was used to develop a number of programs for the development of preschool educational institutions in Barnaul and proved to be a very productive form of developing basic ideas and determining directions for the development of institutions. An essential condition for its effective implementation is the maximum attraction or delegation of the initiative to the teaching staff. In fact, the consultant or project manager is facilitating the production of the maximum number of ideas based on the information about the state of the preschool institution that was collected at the analytical and diagnostic stage of the activity.
1.3. Programming the development of a preschool educational institution
DOW development program - a normative model of joint activity of a group or many groups of people, which determines: a) the initial state (mode) of a preschool educational institution, b) the image of the desired future (a qualitatively new state of the system), c) the composition and structure of actions to transform - transfer preschool educational institutions to a qualitatively new condition .
The development program is a regulatory document that regulates the process of transferring preschool educational institutions from their actual state to a qualitatively new level of development.
The components of the development program fix the goal and objectives, problem analysis with the justification of the relevance, novelty and practical significance of the proposed project, the initial scientific and theoretical prerequisites, indicators characterizing the success of achieving the goal, the timing and stages of the program, performers, resource and information support, control over the course implementation of the program, analysis and correction of results.
The main requirements for the development program allow you to model a truly viable project:
1. Relevance and problematic.
2. Predictability (taking into account today's and tomorrow's conditions).
3. Rationality (correspondence of goals, objectives, content, technologies and results).
4. Realism.
5. Integrity.
6. Sensitivity to failures.
7. Personal, social, moral orientation.
8. Heuristic, experimental, innovative approach.
The source of the formation of the mission, strategy and tactics of the development of the institution is the problematic analysis of its activities.
Problem Analysis Algorithm
1. The initial state of the preschool educational institution is fixed: first of all, the results of the institution's activities for the reporting period are evaluated and an examination of the products obtained is carried out in order to determine the compliance of the achieved goals and objectives. Problematic fields are identified at the level of performance results.
2. The content and course of the educational process are analyzed in detail.
3. The conditions for the functioning of the preschool educational institution are analyzed.
The logic of problem analysis
For each of the problems identified in the process of analysis, a tree of goals is built - a system of steps to eliminate contradictions in each of the aspects of the institution's activities: conditions, process, result (see the following diagram).
Building a tree of goals for solving a specific problem

Explanation for the diagram: c - goals, Vc - the leading goal (I get), cA1 - the formation of motivational readiness (I want), cA2 - the formation of theoretical readiness (I can), cA3 - the formation of technological readiness (I do).
One of the forms of training and updating the skills of teachers in the field of designing and implementing an experimental program in a preschool educational institution can be a business game. Below is an example of using the contextual learning format in the process of innovation.
Didactic game "Program for the development of preschool educational institutions" *
The initial stage in the formation of the teacher's competence in the field of pedagogical innovation is considered the transfer of the subject from the state of unconscious incompetence to the state of conscious incompetence. The form of its implementation is a business game, which is carried out at the initial stage of preparation and development of a development program. The business game is aimed at updating/forming the skills to determine the logic and sequence of developing an experimental program for mastering innovation.
Purpose of the game: to master the algorithm for constructing an experimental program in a preschool educational institution.
The purpose of the game interaction: to develop a single decision in the subgroup regarding the sequence of stages in the development of the program.
The object of imitation in the game: a joint meeting of a temporary creative team of teachers of preschool education in order to develop a program for the development of preschool educational institutions.
Preliminary preparation is connected with informing the participants about the essence and purpose of the business game in the educational process, the basic rules, the competencies of the players and the presenter.
To organize the game, it is necessary to form several subgroups of 5-7 people (depending on the size and preparedness of the audience). Approximate set of roles: chairman (leader), generators of ideas, speaker, secretary, opponent, analyst.
The game takes place in several stages:
Stage I (3-5 minutes) preparatory: drawing up a flowchart (game format): (see table 4-7 columns, 17 lines), designation of column headings and filling in the first column "Program creation steps" of the table.
Stage II (5-7 minutes). Each individual in column 2 "Individual assessment" independently determines the order of the elements of the program: 1 - the first element, 2 - the next, ..., 15 - the last element of the program.
Stage III (10-15 minutes). In subgroups, teachers jointly determine the program development algorithm and make a group decision, which is recorded in the "Group assessment" column.
Stage IV (5-10 minutes). Speech by subgroups: the speaker fixes the logic of creating a development program determined by the group, opponents of other subgroups ask clarifying and problematic questions regarding the content of the speech.
Format of the business game "Program for the development of preschool educational institutions"
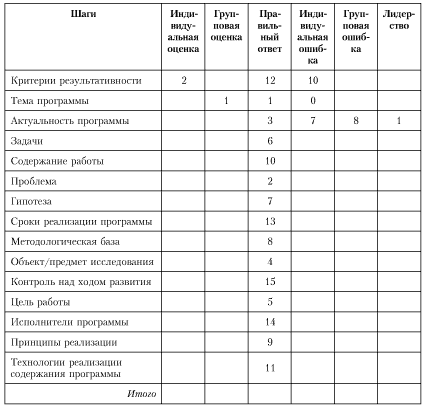
Stage V (10-15 minutes). Processing of results. The column "Correct answer" specifies the sequence of steps in the development of the program. After the first three columns are filled in, the following columns are calculated:
“Individual error”: subtract the value in the corresponding row of the “Correct answer” column from the value of the corresponding row of the “Individual assessment” column, place the difference without a minus sign in the corresponding row of the “Individual error” column (for example, according to performance criteria: 2 - 12 = 10);
"Group error": the same algorithm of actions - the difference in the values in the corresponding rows of the "Group assessment" and "Correct answer" columns is calculated and placed in the "Group error" column (for example, for the program topic: 1 - 1 = 0);
"Leadership": the "subtraction" action is performed with the values in the corresponding rows of the "Individual Error" and "Group Error" columns, the difference without the "minus" sign is placed in the "Leadership" column (for example, for the relevance of the program: 7 - 8 = 1) .
The last action is to calculate the sum for each of the last three columns "Individual error", "Group error", "Leadership", the value of which is placed in the corresponding column of the "Total" row.
Interpretation of the results: if you scored less than 60 points in the corresponding column "Individual error", "Group error" of the "Total" row, then this result is considered to be optimal. You are competent enough to design a development program either on an individual or group level.
The severity of leadership qualities is determined by the rating scale:
less than 20 points: you have pronounced leadership qualities;
20-30 points: you have a fairly high level of leadership;
31-40 points: you have the makings of a leader, but you do not strive to show them;
more than 40 points: you are characterized by a position of conformism.
Stage VI (10 minutes). The group discussion is intended to determine the main accents and priorities in the development of the program, to develop a common point of view on the sequence of steps in its creation.
Stage VII (10 minutes). Reflection of the results and the process of interaction in the game allows teachers to update their own meanings and values, to comprehend the proposed content of the game situation.
1.4. Algorithms for developing a development program for preschool educational institutions
Algorithmizing the process of developing and implementing the development program for the preschool educational institution makes it possible to alleviate the organizational costs of transferring the preschool educational institution to the development mode. The main point in choosing one or another algorithm is to resolve the issues of how the potential of the preschool educational institution allows you to determine the development strategy and identify what problems exist in the preschool educational institution that impede its transition to a qualitatively new level of life activity. Depending on the available answers, for example, to the first question, a strategy is chosen to deepen the problem analysis for an already defined development perspective. If the problems are more or less defined, and the strategy has not yet been formulated, then one should start by defining a development strategy, and then it is necessary to clarify and rank the problems in the preschool educational institution that make it difficult to achieve the indicated ideal goal (see Table 5).
Sample Format for Designing a Development Program
The proposed grounds for analyzing the activities of a preschool educational institution are the organizational basis for developing a development program using the algorithms below.
Algorithm 1 (managerial)
The process of developing a development program can be represented in the logic of management functions.
Analysis (analytical and diagnostic): diagnosis of the initial situation (fixing problems in the state of the preschool educational institution), search for directions and ideas for development (ideal model of the preschool educational institution), building a program to transfer the preschool educational institution to the development mode. Organizational work is aimed at determining the main methodological and methodological approaches to planning and implementing a development program; systematization and generalization of the internal experience of the activity of the preschool educational institution, coordination of the development program with the educational authorities.
Planning (planning and prognostic): determining the ideal model of the future system and the algorithm for transferring the preschool educational institution to the desired state - determining the available and additional resources for transferring the preschool educational institution to the development mode, developing indicators for monitoring the transfer of the preschool educational institution to the development mode; creation of an integrative basis for the activities of all specialists within the framework of pilot programs.
Organization (organizational and executive): creating conditions that ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of the work of all participants in the experiment, establishing cooperation with interested organizations, providing scientific and advisory support for the experiment: implementing experimental programs; involvement of parents, specialists of social institutions of childhood, teachers of preschool educational institutions and children in a single creative productive activity.
Control (control and adjustment): organization of current and final control (monitoring of the progress and results of the experiment); carrying out timely correction and regulation of the course of the experiment based on the data obtained; collection, processing and interpretation of data; organization of the reflexive activity of the participants in the experiment.
Generalization of the results of the experiment, their verification: substantiation of reliability and reliability. Preparation of a managerial decision on the course of the experiment, reviewing the work, methodological recommendations for teachers working in the innovation mode, recommendations for disseminating experience. Dissemination of experience in the framework of new projects and programs in preschool educational institutions. Transfer of preschool educational institution to the status methodological center on the stated problem of working with children from socially disadvantaged families.
Algorithm 2 (meaningful)
All work on the preparation of the development program is represented by 6 blocks:
1.
Analytical block: preparation of an information statement on the state of the preschool educational institution in order to conduct a comprehensive analysis of its activities.
Structure and approximate content of the certificate: a) general information about the establishment (regulatory framework, founders; characteristics of the building, the number of groups-sets; b) analysis of the social situation of development (information about the microdistrict, infrastructure, external relations); c) information about the group of pupils (number, gender and age characteristics, group size); d) information about the team of teachers (experience, qualifications, gender and age characteristics, special merits); e) analysis of the basic spaces of the preschool educational institution and the results of activities for the reporting period, identification of development prospects and problems; f) additional information (merits, traditions of the team).
2. Target block: formation of a set of ideas and development priorities, determination of development goals and objectives. As a rule, development targets are selected based on the definition of the mission of the preschool educational institution (its philosophy), as well as basic values based on the analysis of the social order and the specification of parents' requests for educational services of the preschool educational institution.
3. Content block: associated with the development of directions and content of innovation. The implementation of the set goal and the solution of the tasks identified in the previous block are associated with the specific content of the activity (what is being mastered, what changes occur due to the introduction of innovations, etc.).
4. Technological block: the scope of work is determined, the methods, forms, means of activity within the framework of the managing and executing programs are specified, the performers, time, place of activity and technologies of their work are indicated in detail.
5. The effective block fixes the expected result at the level of the measured indicators of goal achievement. The criteria for the effectiveness of activities for the transfer of preschool educational institutions to the development mode are determined, the qualitative indicators of the new state are described.
6. Expert block: in conclusion, the proposed project is subject to examination by experts - usually external specialists who are competent in the problem being developed. The results of the analysis can be drawn up in the form of a review of the program or an analytical note containing a conclusion on the feasibility, relevance and novelty, as well as the reality of the project proposed for implementation.
The publication of the article was made with the support of the Internet project "IN DEBT". By visiting the website of the Internet project "IN DEBT" at http://vdolg.info, you will find a convenient service that will help you borrow money at interest from a private person in a private bank in the shortest possible time. Thanks to the services of the site of the independent financial consultant "VDOLG", it has become really easy to get a loan or a cash loan, which allows you to make purchases or meet your urgent cash needs without waiting for a salary.

* In accordance with the psychological and pedagogical principles of design and the structure of the business game, the proposed format has been developed. Materials of the methodological manual were used: Bobrova M.P.. Didactic training of teachers of preschool institutions in the context professional activity: Toolkit. Barnaul: Publishing house of BSPU, 1997. S. 48-57.
Photo by A. Stepanov
Children (educational areas)
Directions for the development and education of children
(educational areas)
Tasks for their implementation
Social and communicative development
Assimilation of norms and values accepted in society, including moral and ethical values; development of communication and interaction of the child with adults and peers; - the formation of independence, purposefulness and self-regulation of one's own actions;
Development of social and emotional intelligence, emotional responsiveness, empathy, the formation of readiness for joint activities with peers, the formation of a respectful attitude and a sense of belonging to one's family and to the community of children and adults in the Organization;
Formation of positive attitudes towards various types of work and creativity;
Formation of the foundations of safe behavior in everyday life, society, nature.
cognitive development
Development of children's interests, curiosity and cognitive motivation;
Formation of cognitive actions, formation of consciousness;
Development of imagination and creative activity;
Formation of primary ideas about oneself, other people, objects of the surrounding world, about the properties and relations of objects of the surrounding world (shape, color, size, material, sound, rhythm, tempo, quantity, number, part and whole, space and time, movement and rest , causes and consequences, etc.), about the small homeland and Fatherland, ideas about the socio-cultural values of our people, about domestic traditions and holidays, about the planet Earth as common house people, about the peculiarities of its nature, the diversity of countries and peoples of the world.
Speech development
Possession of speech as a means of communication and culture;
Enrichment of the active dictionary;
Development of coherent, grammatically correct dialogic and monologue speech;
Development of speech creativity;
Development of sound and intonation culture of speech, phonemic hearing;
Acquaintance with book culture, children's literature, listening comprehension of texts of various genres of children's literature;
Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for literacy.
Artistic and aesthetic development
Development of the prerequisites for value-semantic perception and understanding of works of art (verbal, musical, visual), the natural world;
The formation of an aesthetic attitude to the world around;
Formation of elementary ideas about the types of art;
Perception of music, fiction, folklore;
Stimulation of empathy for the characters of works of art;
Implementation of self creative activity children (fine, constructive-model, musical, etc.).
Physical development
Gaining experience in the following types of children's activities: motor, including those associated with the implementation of exercises aimed at developing such physical qualities as coordination and flexibility; contributing to the correct formation of the musculoskeletal system of the body, the development of balance, coordination of movement, large and small motor skills of both hands, as well as the correct performance of basic movements that do not harm the body (walking, running, soft jumps, turns in both directions), the formation of initial ideas about some sports, mastering outdoor games with rules;
Formation of purposefulness and self-regulation in the motor sphere;
The formation of the values of a healthy lifestyle, mastering its elementary norms and rules (in nutrition, motor mode, hardening, in the formation of good habits, etc.).
Source
Source edu.mari.ru
Comparative analysis of FGT and GEF DO
GEF requirements
The program determines the content and organization of the educational process for children of age and is aimed at
Formation of a common culture,
Development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities,
Formation of prerequisites for educational activities that ensure social success,
Preservation and strengthening of the health of preschool children,
Correction of shortcomings in the physical and (or) mental development of children.
1) increasing the social status of preschool education;
2) ensuring by the state of equal opportunities for each child in obtaining a quality preschool education;
3) ensuring state guarantees of the level and quality of preschool education based on the unity of mandatory requirements for the conditions for the implementation of educational programs for preschool education, their structure and the results of their development;
4) maintaining the unity of the educational space of the Russian Federation regarding the level of preschool education.
Integrative qualities
Targets - social and normative age characteristics of the child's possible achievements at the stage of completing the level of preschool education
Targets are not subject to direct assessment, including in the form pedagogical diagnostics(monitoring), and are not the basis for their formal comparison with the real achievements of children.
Principles
Scientific validity and practical applicability;
Completeness, necessity and sufficiency;
The unity of educational, developing and teaching goals and objectives;
Integration of educational areas;
Complex-thematic principle of building the educational process;
Solving program educational tasks in joint activities of age-appropriate forms of work with children. The main form of work with children of preschool age and the leading activity for them is the game.
Clause 1.2. (legislation of the Russian Federation):
1) support for childhood diversity; preservation of the uniqueness and intrinsic value of childhood as an important stage in the overall development of a person, the intrinsic value of childhood;
2) the personality-developing and humanistic nature of the interaction between adults (parents (legal representatives), pedagogical and other employees of the Organization) and children;
3) respect for the personality of the child;
4) implementation of the Program in forms specific for children of this age group, primarily in the form of a game ...
Clause 1.4. Basic principles of preschool education:
1.full living by the child of all stages of childhood, enrichment (amplification) of child development;
2. building educational activities based on the individual characteristics of each child, in which the child himself becomes active in choosing the content of his education, becomes the subject of education;
3. assistance and cooperation of children and adults, recognition of the child as a full-fledged participant (subject) of educational relations;
4. support for the initiative of children in various activities;
5. cooperation of the Organization with the family;
6.introducing children to socio-cultural norms, traditions of the family, society and the state;
7. formation of cognitive interests and cognitive actions of the child in various activities;
8. Age appropriateness of preschool education;
9. taking into account the ethno-cultural situation of children's development
Structuring content
4 child development lines, 10 educational areas
Social and communicative development;
Early and preschool age
Monitoring the effectiveness of educational activities
Monitoring system achievement by children of the planned results of mastering the Program (assessment of the final and intermediate results of mastering the Program), allows you to assess the dynamics of children's achievements and include a description of the object, forms, frequency and content of monitoring
Clause 3.2.3. .
Such an assessment is carried out by a teacher within the framework of pedagogical diagnostics (assessment of the individual development of preschool children, associated with the assessment of the effectiveness of pedagogical actions and underlying their further planning).
The results of pedagogical diagnostics (monitoring) can be used exclusively for solving educational problems.
If necessary, psychological diagnostics of the development of children is used (identification and study of the individual psychological characteristics of children), which is carried out by qualified specialists (educators-psychologists, psychologists).
The structure of the educational program
Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of children brought up in an educational institution;
Priority areas of activity of an educational institution for the implementation of the main general educational program of preschool education;
Goals and objectives of the activity of an educational institution for the implementation of the main general educational program of preschool education;
Features of the implementation of the educational process (national-cultural, demographic, climatic and others);
Principles and approaches to the formation of the Program.
Explanatory note:
1.goals and objectives of the implementation of the Program (clause 2.4)
2.principles and approaches to the formation of the Program (clause 1.4)
3. characteristics significant for the development and implementation of the Program, including characteristics of the developmental features of children of early and preschool age.
Organization of the regime of stay of children in an educational institution
Planned results of mastering the main general educational program of preschool education by children;
The system for monitoring the achievement by children of the planned results of the development of the Program.
2. Part of the Program formed by participants in educational relations reflects:
1) species diversity of institutions, the presence of priority areas of activity, including ensuring equal starting opportunities for teaching children in general educational institutions ... (except for activities for the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with handicapped health);
2) the specifics of the national-cultural, demographic, climatic conditions in which the educational process is carried out.
1. Mandatory part of the EP: in accordance with the directions of the child's development, presented in five educational areas: social and communicative development; cognitive development; speech development; artistic and aesthetic development; physical development;
- The part formed by the participants of educational relations: may include various directions chosen by the participants of educational relations from among partial and other programs and / or created by them independently.
2. Description of variable forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the Program, taking into account age and individual characteristics, the specifics of their educational needs and interests.
-Part formed by the participants of educational relations should take into account the educational needs, interests and motives of children, their families and teachers and, in particular, may be focused on:
u the specifics of national, sociocultural and other conditions in which educational activities are carried out;
u choosing those partial educational programs and forms of organizing work with children that best meet the needs and interests of children, as well as the capabilities of the teaching staff;
established traditions of the Organization or Group.
3. Description of educational activities for the professional correction of developmental disorders in children if this work is provided for by the Program.
In the case of organizing inclusive education on the grounds, unrelated children with disabilities, highlighting this section is optional; in the case of his selection content this section is determined by the Organization on one's own.
Organization section
If the mandatory part of the Program complies with exemplary program, it is made in the form of a link to the corresponding sample program. The mandatory part must be presented in full in accordance with paragraph 2.11 of the Standard, if it does not match one of the sample programs.
- Part of the Program formed by participants in educational relations, can be represented as links on the relevant methodological literature, allowing you to get acquainted with the content of the educational relations chosen by the participants partial programs, methods, forms of organization of educational work (clause 2.12) .
Additional section
The text of a brief presentation of the OP, focused on parents (legal representatives) of children and available for review:
Age and other categories of children targeted by the Program of the Organization, including categories of children with disabilities, if the Program provides for the specifics of its implementation for this category of children;
Sample programs used;
Characteristics of the interaction of the teaching staff with the families of children.
Conditions for the implementation of the OOP
Formation of professional interaction between teachers and children
Maintaining the mental health of pupils
Ensuring the unity of educational, teaching and developing goals and objectives of the educational process
Taking into account the gender specificity of the development of preschool children
Ensuring continuity with exemplary basic general education programs of primary general education
Building interaction with the families of pupils
Creation of a system of organizational and methodological support of the EP
The division of pupils into age groups
The focus of organizational and methodological support of the main general educational program of preschool education on working with children in the zone of proximal development and on organizing independent activities of pupils
Compliance with the requirements for the interaction of the educational institution with parents
3.2.1. Psychological and pedagogical conditions:
1) respect of adults for the human dignity of children, the formation and support of their positive self-esteem, confidence in their own abilities and abilities;
2) the use in educational activities of forms and methods of working with children that correspond to their age and individual characteristics (inadmissibility of both artificial acceleration and artificial slowdown in the development of children);
3) building educational activities based on the interaction of adults with children, focused on the interests and capabilities of each child and taking into account the social situation of his development;
4) support by adults of a positive, friendly attitude of children to each other and the interaction of children with each other in various activities;
5) support for the initiative and independence of children in activities specific to them;
6) the opportunity for children to choose materials, types of activity, participants in joint activities and communication;
7) protection of children from all forms of physical and mental abuse;
8) support of parents (legal representatives) in raising children, protecting and strengthening their health, involving families directly in educational activities.
3.2.2. To receive a quality education without discrimination children with disabilities are created the necessary conditions for the diagnosis and correction of developmental disorders and social adaptation, providing early correctional assistance based on special psychological and pedagogical approaches and the most suitable languages, methods, ways of communication and conditions for these children.
3.2.3. During the implementation of the Program, an assessment of the individual development of children can be carried out . Such an assessment is carried out by a teacher within the framework of pedagogical diagnostics (assessment of the individual development of preschool children, associated with the assessment of the effectiveness of pedagogical actions and underlying their further planning). The results of pedagogical diagnostics (monitoring) can be used exclusively for solving educational problems.
3.2.4. The occupancy of the Group is determined taking into account the age of the children, their state of health, the specifics of the Program
3.2.5. The conditions necessary to create a social situation for the development of children, corresponding to the specifics of preschool age ....
3.2.6. In order to effectively implement the Program, conditions must be created for:
professional development pedagogical and executive employees, including their additional professional education;
advisory support for teachers and parents…
3.2.7. To work with children with disabilities, mastering the Program together with other children in Groups of combined orientation, conditions should be created in accordance with the list and plan for the implementation of individually oriented corrective measures.
3.2.8. The organization should create opportunities:
1) to provide information about the Program to the family and all interested persons involved in educational activities, as well as the general public;
2) for adults to search, use materials that ensure the implementation of the Program, including in the information environment;
3) to discuss with the parents (legal representatives) of children of issues related to the implementation of the Program.
3.2.9. The maximum allowable amount of educational load..
Personnel conditions
The level of qualifications of pedagogical and other employees
Continuity of professional development of teaching staff
3.4. Requirements for personnel conditions for the implementation of the Program.
3.4.1. The implementation of the Program is provided by the leading, pedagogical, educational and auxiliary, administrative and economic employees of the Organization.
3.4.2. The teaching staff implementing the Program must have the basic competencies necessary to create the conditions for the development of children, indicated in clause 3.2.5 of this Standard.
3.4.3. When working in Groups for children with disabilities, the Organization may additionally provide for the positions of pedagogical workers who have the appropriate qualifications to work with these children's health limitations.
3.4.4. When organizing inclusive education:
when included in the Group of children with disabilities, additional pedagogical workers who have the appropriate qualifications to work with these health limitations of children may be involved in the implementation of the Program.
Logistics conditions
Material perm371.ru
1. List the priority areas for the development of the preschool education system.
2. What are the main regulations defining new priorities for the development of preschool education.
4. Why was the standard of preschool education not approved in the field of preschool education, as in?
5. Name the main 6 directions of the National Strategy of Action for Children for 2012-2017.
1 .List priority areasi development system of preschool abouteducation
Answer:
The Russian government is currently paying a lot of attention to preschool education. This is evidenced by the current programs of the FTsPRO - 2011-2013, 2011-2015, created in 2015-2017, 2020, 2025. The state policy has given priority functions in strategic development to the construction of new preschool educational institutions according to new standard projects, variable preschool education, including variable forms - kindergartens supervision and rehabilitation; compensatory type; child development centers; educational institutions " Primary School- kindergarten”, “landing” groups, adaptation groups “nursery + mother”, groups of short-term stay of children in kindergarten and other institutions, etc.
Ensuring state guarantees for the availability of preschool education and its new quality are the most important areas for the modernization of Russian and regional education. Accessibility is characterized by the possibility of choosing a kindergarten, its quality - by the child's opportunities and abilities to master educational programs at subsequent levels of education.
A strategy for the development of the system of preschool education has been developed, which is being implemented in several directions.
First direction– planning the reconstruction of buildings and increasing the number of groups, construction and commissioning of new kindergartens. Re-profiling of objects used in education for other purposes.
Second direction- the introduction of paid additional services in the preschool educational institution in accordance with the social request: health, development, educational, organizational, etc.
third direction- an increase in the number of groups in existing preschool educational institutions of a compensatory and combined orientation, equipping groups with specialized equipment, which will allow for correction at the early stages of identifying problems and help create equal starting conditions for the child.
Fourth direction- organization of the work of groups of short-term and round-the-clock stay of children in preschool educational institutions.
Fifth direction- search for new variable forms of work with unorganized children - a combined, compensatory and health-improving orientation, the provision of services at home, distance learning for children with disabilities. Approbation of innovative models - a group of comfortable stay of children on a self-supporting basis.
The above directions will contribute to the availability and quality of educational services, remove the existing differences in readiness to master the programs of preschool and school education
2. What are the main regulatory documents that define new priorities for the development of preschool education.
Answer:
"Law on education" of the Russian Federation.
Decree of the Government of the Stavropol Territory dated December 16, 2009 No. 303P “On the regional target program “Development of Education in the Stavropol Territory for 2010-2013.” (As amended by the Decrees of the Government of the Stavropol Territory No. 14P dated January 20, 2010, No. 272P dated August 18, 2010, No. 444P dated December 15, 2010, No. 110P dated April 4, 2011, No. 221P dated June 16, 2011, No. 382P dated September 21, 2011, dated 26.10.11 No. 433P) a subprogram on preschool education was adopted, which became a guide to action for the modernization of the regional system of preschool education.
3. What is the most important direction of modernization of Russian and regional education?
Answer:
The modernization of preschool education in the region is connected with the demographic factor and the problem of placing children in kindergartens. There is difficulty in accessing preschools for children with disabilities (HIA). Taking into account the problems, the self-governing bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have developed a strategy for the development of the system of preschool education, which is being implemented in several directions.
Ensure the availability of high-quality educational services to the population, improve the skills of trainees in advanced training courses (CPC) in the field of modernization of preschool education based on modern management models and disseminate the positive experience of the system of preschool education of the municipalities of the Stavropol Territory to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
4. Why didn’t they approve the standard of preschool education in the field of preschool education, as in school?
Answer:
Standards - the realities of modern preschool education, define a certain general matrix - the content of the requirements for educational services, quality, goals and results of preschool education. Regarding preschool childhood and the age of the child, at first glance, the standard cannot be acceptable (this was the first feeling when developing the Temporary Requirements). But in the process of their approbation, a taste of creativity appeared, and with further certification, accreditation, licensing, the preschool educational institution acquired, to put it mildly, a distorted formalized character over time.
Standards can't lower variability of preschool education and impose a unified educational program. The philosophy of new educational standards in preschool educational institutions, general education and vocational schools consists precisely in expanding educational freedoms and services, providing an educational environment for an individual trajectory of personal development, for choosing content and technological content for self-realization, and gaining experience to study and work.
5. What are the main 6 directions of the National Strategy of Action for Children for 2012-2017.
Answer:
Availability of quality education and upbringing, cultural development and information security of children;
Child-friendly healthcare and healthy lifestyle life;
Equal opportunities for children in need of special state care;
Creation of a system for protecting and ensuring the rights and interests of children and child-friendly justice;
Children are participants in the implementation of the National Strategy.
see also:
Material from the site aplik.ru
Modern problems of preschool education,
Phase I Call"
(awakening of existing knowledge of interest in obtaining new information)
Pay attention to the topic title Contemporary Issues preschool education, trends in its development and directions of reform(on the screen)
and answer the question: Is this question relevant for college graduates? Why?
Frontal conversation
1. When did a unified program for kindergartens appear in our country?
In the early 60s. 20th century a unified comprehensive program educating children in kindergarten which was a mandatory document in the work of preschool educational institutions of the USSR. The leading research institutes of preschool education of the country and the leading departments of preschool pedagogy worked on the content of this program.
2. What are the advantages of the Soviet system of preschool education?
And although Soviet preschool education was focused on the demands of the system, it had its own advantages: systemic character, general availability, public funding.
3. What changes took place in the late 80s and early 90s of the last century?
On the threshold of the 21st century, The concept of preschool education, the authors of which were teachers Davydov V. and Petrovsky V..
This Concept contains the basic principles of preschool education in Russia:
- Humanization(education of the humanistic orientation of the personality of a preschooler, the basics of citizenship, diligence, respect for human rights and freedoms, love for the family, nature).
- Developmental nature of education(orientation to the personality of the child, preservation and strengthening of his health, installation on mastering the ways of thinking and activity, development of speech).
- Deideologization of preschool education(a priority universal values, rejection of the ideological orientation of the content of kindergarten educational programs).
- Differentiation and individualization of education and training(development of the child in accordance with his inclinations, interests, abilities and capabilities).
- A variety of variable or alternative preschool education programs have emerged.
Today we will get acquainted with the issues that concern every preschool teacher, parents of preschoolers, scientists, officials who are directly related to preschool education. Modern problems of preschool education, trends in its development and directions of reform.
Phase II Understanding the content" (getting new information)
Getting acquainted with a number of today's materials, try to analyze the information according to the PMI methodology (plus-minus-interesting). (See Appendix 2)
It is used in the technology "Development of critical thinking"
We learn to work with information, to analyze various aspects of phenomena.
Edward de Bono Edward de Bono; genus. May 19, 1933, Malta) - British psychologist and writer, expert in the field of creative thinking, doctor of medicine, creator of the concept of "out-of-the-box thinking".
Students keep a brief record of the material, make notes on the tablets according to the PMI method (plus-minus-interesting)
Topic: Modern problems of preschool education, trends in its development and directions for reform
1. Modern problems of preschool education. Let's discuss the problems first. Please advise, I think that all these problems are familiar to you:
1. Given the gradually improving demographic situation in the country, the demand for kindergarten services is constantly growing. In large cities of Russia there is a clear shortage of preschool educational institutions.
There are not enough places in preschool educational institutions. Parents enroll their child in kindergarten immediately after birth, and this is not always a guarantee that he will get there.
At present, 400,000 children in Russia are waiting for their turn to enter a kindergarten. Before the state, first of all, it is worth the task of accessibility of preschool education for all segments of the population.
2. The need of preschool educational institutions for qualified teaching staff. The preschool administration is forced to reduce the requirements for staff in terms of their professional and experience in working with children.
3. Currently, in the Russian Federation, increase in the number of children with disabilities: twice as compared to 2002, "children with special educational needs" should not be isolated in society, hence the need for inclusive education.
4. The features of the sociocultural environment are changing modern society -this is multiculturalism, multinationality, polyethnicity. Therefore, it is necessary to build multicultural educational environment of preschool educational institutions, creation of a multicultural educational space; it is necessary to look for new technologies for the upbringing and development of children, including children who do not speak Russian well enough.
5. The need for diversification**(assignment to students - the concept is entered in the plate "PMI", column "Interesting".look it up in a dictionary), i.e., sufficient variety of types and types of institutions, educational services and approaches to their implementation in order to meet the diverse and versatile needs of participants in the educational process in preschool educational institutions.
6. Transition of most preschools from operating mode to search mode and to development mode. The need for a raise methodological competence preschool teachers , students pedagogical educational institutions.
7. Currently changes in the social order of parents, their requirements for the services provided preschool institutions. If for many decades health care and childcare were considered for many parents as the main areas of work of kindergartens, today more and more requirements are placed on educational programs basic and additional education.
8. Continuity between preschool and junior school age is often determined by the presence or absence of certain knowledge in academic subjects. This leads to early learning for children.
It must be admitted that it is precisely this approach that can be conditionally designated as narrowly pragmatic, oriented towards the needs of the system, and not the child himself. Modern pedagogical research shows that the main problem of preschool education is the loss of vivacity, the attractiveness of the process of cognition. The number of preschool children who do not want to go to school is increasing; the positive motivation for classes has decreased, the performance of children is falling.
9. Educators are embarrassed by the absence rigid objectivity, need integration educational areas. But it is only in integrated content that preschool children are free to make wide choices and express their as yet unstructured interests and creativity.
10. Strong in Russian pedagogy the emphasis was usually placed on the game forms and methods of teaching children, and not on free play. However, it is very important for development to be played by a child, not an adult. What if it was just a game, and not its imitation.
11. Informatization of preschool education- the process is objective and inevitable. In kindergartens, a new educational environment, there are high-tech information tools for teaching and developing preschoolers, the interest of teachers and preschool education specialists in these technologies and the possibilities of using them in their professional activities is growing.
However, not all teachers are ICT-savvy. This complicates the use of ICT in working with children or makes it impossible for a modern channel of communication with parents and other members of the pedagogical community.
2. Trends in the development of preschool education at the present stage
The development of preschool education is one of the priority development goals Russian education at the present stage.
For lining up variable education it is necessary, first of all, determine the invariant, i.e. obligatory essential core of the content of education. In his capacity are standards. In what direction was work carried out in the field of preschool education?
1. "Federal state requirements for the structure of the main general educational program of preschool education" Published: March 5, 2010 in "RG" - Federal issue No. 5125 Effective: March 16, 2010
2. "Federal state requirements for the conditions for the implementation of the main general educational program of preschool education" Published: November 21, 2011 in "RG" - Federal issue No. 5637 Effective: December 2, 2011
Federal Law "On Education in the Russian Federation". Adopted by the State Duma on December 21, 2012 Approved by the Federation Council on December 26, 2012 entered into force on September 1, 2013.
The enactment of the Federal Law "On Education in the Russian Federation" marked new stage in the development of the domestic system of preschool education. Pre-school education received the status of the first stage of education, which required a change in the regulatory framework for its implementation.
On the one hand, this recognition of the importance of early childhood education in the development of the child, on the other hand, increasing the requirements for preschool education, including through the adoption of the federal state educational standard for preschool education .
4. The most important innovation of a fundamental nature is the creation of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education (FSES DO) - a document that has no analogues in Russian history.
The development of the standard was carried out with January 30, 2013 year by a working group of leading experts in the field of preschool education under the leadership of the director of the Federal Institute for the Development of Education Alexander Asmolov.
June 2013 year, the GEF project of preschool education was presented to the public public discussion. Over 300 comments and suggestions received on the draft standard were considered at a meeting of the Council of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation on Federal State Educational Standards on July 3, 2013.
In accordance with the decision of the Council, the draft Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education was finalized and submitted for reconsideration. Based on the conclusions of 11 expert organizations and the recommendation of the working group of general education Council of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation on Federal State Educational Standards On August 28, 2013, he decided to approve the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education.
Introduction of GEF DO into practice will require the implementation of a number of activities, determining their nature and sequence. It is obvious that there should be developed "road maps"* at the level of the country, regions, specific institutions, including both material and technical equipment, and methodological support for the modernization of the system of preschool education.
The assignment for students is to find out the meaning of the concept of "Roadmap" (Internet http://ru.wikipedia.org) The concept is entered in the "PMI" plate, the "Interesting" column. (See Appendix 3)
At the same time, the effectiveness of the implementation of all measures will be largely determined by understanding the content of the Federal State Educational Standard, understanding and accepting the ideas of the authors of this document.
Viewing a fragment of the presentation in the international multimedia press center RIA Novosti of the project of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education.http://pressria.ru/media/20130614/601783488.html June 14, 2013
Today you will get acquainted with the latest version of the Federal State Educational Standard, which, according to experts, was approved on August 28.
Please choose on which information carrier it is more convenient for you to work - on paper or in electronic form. The teacher offers materials - the draft Federal State Educational Standard on paper or on the website http://minobrnauki.rf.pdf.
Questions for familiarization with the Federal State Educational Standard of preschool education:
1. The main components of the educational standard, structure (use the abbreviations GEF DO, OOP DO).
2. Basic values of Russian preschool education.
3. Principles of preschool education.
Material from the site ext.spb.ru


